The 3D modeling involves creating a digital representation of a 3-dimensional object using specialized software. Beyond shape, you can define surface textures, colors, and lighting to create a realistic or stylized visual. The 7 types of 3D modeling are: Wireframe modeling, Surface modeling, Solid modeling, Polygonal modeling (or 3D Sculpting), Sculpting (or Digital sculpting), NURBS modeling, and BIM modeling.
From the automotive industry to the gaming industry, film, retail, manufacturing, marketing, and other industries utilize this technique to enhance customers’ experience. 3D artists use 5 popular software, such as Autodesk 3Ds Max, Blender, Autodesk Maya, ZBrush, and SketchUp to create these creative works.
And to maintain creativity flow and aesthetics, a professional 3D modeler follows 10 simple workflows, such as planning concept, creating a basic shape, modeling the shape, refining, UV mapping, texturing & shading, rigging, lighting & environment setup, rendering, and exporting after reviewing.
What you’ll learn in this article
- 1 What is 3D Modeling?
- 2 How Does Digital 3D Modeling Work?
- 3 What is 3D Modeling Used for?
- 4 What are the Different Types of 3D Modeling?
- 5 What is the Best 3D Modeling Software?
- 6 How to Learn 3D Modeling
- 7 How to Make 3D Product Models
- 8 What File Formats are Used in 3D Product Modeling?
- 9 Can Small Businesses Benefit from 3D Product Modeling?
What is 3D Modeling?
3D modeling refers to the process of creating an object’s three-dimensional representation using 3D modeling software (Blender, Maya, SketchUp, etc). The process involves manipulating points, edges, and polygons within a simulated 3D space to define the object’s shape, size, and surface details.
How Does Digital 3D Modeling Work?
Digital 3D modeling works by manipulating points (vertices), edges (lines), and polygons (faces) within a virtual 3D space to construct a mesh that forms the object’s shape. This mesh is then refined with textures, lighting, and other effects to create a realistic or stylized 3D model. Before heading to the detailed working process, pay attention to the 5 core concepts: the building blocks of 3D models (Vertices, Edges, and Polygons), Polygonal Modeling, Curve Modeling & Digital Sculpting, Texture Mapping, and Coordinate system.
Step 1: Conceptualization and Planning
The digital 3D modeling process begins with an idea or reference, such as sketches, photos, or concept art. This stage involves planning the shape, structure, and details of the object to be modeled.
Step 2: Initial Blockout / Basic Shape Creation
Using 3D modeling software, the artist creates simple geometric shapes (primitives) like cubes, spheres, or cylinders to form the rough outline or “block out” of the model.
Step 3: Modeling the Basic Shape
The basic shapes are refined by manipulating vertices, edges, and faces to sculpt the overall form of the object. Techniques like extrusion, beveling, and subdivision are used to add complexity.
Step 4: Detailing and Refinement
Additional details are added to the model, such as intricate surface features, curves, and textures. This may involve sculpting or adding smaller components.
Step 5: UV Mapping and Unwrapping
The 3D surface is “unwrapped” into a 2D plane to create a UV map, which allows textures and colors to be accurately applied to the model.
Step 6: Texturing and Shading
Textures (images or procedural patterns) are applied to the UV map to give the model color, surface detail, and material properties like glossiness or roughness.
Step 7: Rigging (Optional)
For models intended for animation, a digital skeleton (rig) is created to allow movement and deformation.
Step 8: Lighting and Environment Setup
Virtual lights and environmental settings are configured to simulate realistic or stylized illumination on the model.
Step 9: Rendering
The final model is processed by a rendering engine to produce 2D images or animations, incorporating lighting, shadows, reflections, and textures.
Step 10: Final Review and Export
The completed model is reviewed, adjusted if necessary, and exported in appropriate file formats for use in games, films, VR, manufacturing, or other applications.
What’s the Difference Between 2D and 3D Modeling?
The key differences between 2D and 3D modeling are as follows:
| Aspect | 2D Modeling | 3D Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating flat images or drawings with only height and width dimensions. | Creating digital objects with height, width, and depth, gives them volume and realism. |
| Representation | Flat shapes, lines, curves, and images on a single plane (X and Y axes). | Volumetric shapes that can be rotated, viewed, and edited from any angle (X, Y, and Z axes). |
| Tools & Software | Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, Photoshop (for 2D graphics), and AutoCAD 2D Drafting. | Blender, Maya, 3Ds Max, SolidWorks, Fusion 360, ZBrush. |
| Use Cases | Logos, icons, UI/UX designs, schematics, 2D floor plans, and illustrations. | Product modeling, animation, games, AR/VR, architectural visualization, engineering, 3D printing. |
| Visual Output | Flat images, drawings, or illustrations with no real depth or volume. | Realistic models with textures, lighting, and perspective that mimic real-world objects. |
| Learning Curve | Generally easier and faster for beginners to start with. | Steeper learning curve due to software complexity and understanding of 3D space. |
| Editing | Modifications involve changing lines, shapes, colors, or layers. | Edits involve manipulating meshes, vertices, edges, surfaces, textures, and lighting. |
| File Formats | .AI, .PSD, .SVG, .EPS, .PNG, .JPG | .OBJ, .FBX, .STL, .BLEND, .MAX, .3DS |
| Cost & Resource Intensity | Less hardware-intensive; runs smoothly on most computers. | More hardware-intensive; requires powerful GPUs and RAM for modeling and rendering. |
| Output Purpose | Print design, digital illustrations, web graphics. | Digital assets for animations, games, AR/VR, manufacturing prototypes, and product visualization. |
What is the Difference Between 3D Modeling and 3D Sculpting?
The key differences between 3D modeling and 3D sculpting are as follows:
| Notes | 3D Modeling | 3D Sculpting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of creating 3D objects by manipulating geometry (vertices, edges, faces) using tools like extrusion, bevel, and loop cuts. | The process of creating and refining 3D shapes by digitally “sculpting” like clay using brushes to add or subtract volume and details. |
| Approach | Technical and structured, building models with clean topology and precise control over shape. | Artistic and organic, shaping models freely to create detailed, high-resolution forms. |
| Best for | Hard-surface objects: products, architecture, machinery, furniture, vehicles. | Organic objects: characters, creatures, detailed decorative elements, complex anatomical forms. |
| Software | Blender (Edit/Modeling mode), Maya, 3Ds Max, SolidWorks, Fusion 360. | ZBrush, Blender (Sculpt mode), Mudbox, Nomad Sculpt. |
| Workflow | Focuses on clean topology, geometry accuracy, and low to mid-poly modeling for animation, CAD, and games. | Focuses on high-resolution mesh detailing for realism, often retopologized later for animation or game use. |
| Topology control | Requires careful topology planning throughout modeling. | Retopology is usually done after sculpting to create an optimized, animatable mesh. |
| Polycount | Generally lower to mid-level polycount with optimized edge loops for performance and rigging. | Very high polycount models (millions of polygons) to capture fine surface details. |
| Detail Creation | Uses modifiers and modeling tools for form refinement; less ideal for micro details. | Uses brushes (clay build-up, crease, smooth) to create micro details like pores, wrinkles, and intricate textures. |
| Output Use | Game assets, product design, architectural visualization, and manufacturing. | Character design, concept art, cinematic models, game and film high-poly assets, and 3D printing detailed figures. |
What is 3D Modeling Used for?

3D modeling is a versatile technique for designing, visualizing, developing, and refining intricate details structures for many industries, including research, education, entertainment, product manufacturing, and architecture. Here is what it is used for based on industries.
1. Entertainment & Media
3D models are used for pre-visualizing, indicating details, special effect creating, rigging, immersive world & settings designing, and so on. The gaming and entertainment industry uses this technique for gaming character development, virtual environment creation, film, and motion graphics.
2. Product Design & Manufacturing
This 3D model brings manufacturing and product-designing business ideas to light. The digital representation of objects significantly reduces the cost of physical prototyping and helps businesses explore different functionalities, visualization, and further steps.
3. Architecture & Interior Design
In interior and architectural design, three-dimensional modeling is used for conceptualizing architectural design, which is different from traditional hand-drawn methods. As a result, a realistic architectural digital model creation is easier and more efficient for both small and large spaces.
4. Healthcare & Medicine
3D models have revolutionized the medicine and healthcare industry for better patient care. The system provides comprehensive views for research, diagnosis, and treatment segments, and also aids in pre-surgical plans, medical equipment designing, patient communication, and the educational process.
5. Education & Training
The education and Training industry has seen revolutionary changes, thanks to interactive 3D modeling. It has simplified complicated ideas, offered a realistic representation of topics, and provided meticulous guides on different components for the students, enriching their learning process.
6. Marketing & Advertising
3D model is a top-level performer for business marketing approaches. With 3D, Brands provides product visualization, advertising, immersive experiences, product designing, and a virtual demo creation process, boosting engagement rates.
7. Scientific Research & Exploration
For scientific research, 3D modeling is inevitable. It has accelerated the scientific process, for example, scientists can simulate natural phenomena and understand ecology, research human organs and fossils, explore and create celestial bodies, test robotics and artificial intelligence, and so on.
What are the Different Types of 3D Modeling?
The 8 main types of 3D modeling are: Wireframe modeling, Surface modeling, Solid modeling, Polygonal modeling (or 3D sculpting), NURBS modeling, Procedural Modeling, Sculpting (or Digital sculpting), and BIM modeling.
1. Wireframe Modeling
This is the most basic type, representing objects as a network of lines and vertices, showing only the edges and structure of the model without solid surfaces or textures. When you work with large assemblies, viewing models in wireframe mode helps you avoid lag and improves navigation speed. Also, you can edit points and edges directly, making it ideal for early-stage design reviews. You can use this modeling for conceptual design & drafting, CAD, animation, blueprint, model debugging, and so on.
2. Surface Modeling
This type defines the outer surfaces of an object, providing more detail than wireframe modeling. It focuses on the visible faces and curves. Surface modeling uses mathematical definitions, ensuring accuracy in industrial design, especially for parts with aerodynamic or ergonomic requirements. Surfaces can be edited by adjusting underlying curves, making it easier to iterate and refine designs during the conceptual phase.
3. Solid Modeling
Solid modeling represents the entire volume of an object, including its interior. This is often used for creating realistic and functional designs. This modeling is used for creating realistic and functional designs, such as automotive design, aerospace components, consumer product design, industrial styling, and so on.
4. Polygonal Modeling
Also known as Mesh Modeling, Polygonal Modeling creates 3D shapes using smaller components like edges, vertices, faces, triangles, polygons, etc. By manipulating these components a mesh is formed for further work of shapes or structures creation. There are different techniques used for creating polygonal modeling, such as Extrusion, Beveling, Subdivision, Inset, Biset, etc.
The polygonal model is highly effective in rendering, offers a flexible and scalable working process, is adaptable for animation, and users can go for detailed texturing. That’s why it is mostly used in animation, films, video games, 3D printing, AR, VR, and so on.
Is Polygonal Modeling Related to Low-poly, High-poly, and Retopoly?
Low-poly, high-poly, and retoplogy related to polygonal modeling, to be specific, directly with mesh.
Here is how.
- High-Poly: Mesh that is sculpted with voxel-based 3D models among many other modeling techniques. It is used for capturing fine and extreme details, for example, face wrinkles.
- Low-Poly: Mesh having lower poly count or 3D models created from low polygons, still maintaining the overall form of the model, used for models needing real-time rendering.
- Retopology: It is the process of creating new mes, mostly a low poly instead of a high poly, preserving the details of high poly yet reducing the number of polygons, for example: creating 3D models for 3D printing.
5. NURBS Modeling
Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) is a mathematical technique of 3D graphics and computer-aided design (CAD) used for creating simple surfaces, curves, and shapes into complex forms precisely.
The basics of NURBS include control points, knots, weights, parameterization, etc. For its higher accuracy, flexibility, and scalability, it is used in the mechanics, animation, automotive, product design, engineering industries, organic modeling, and architecture industries.
6. Procedural Modeling
In procedural modeling, 3D models are generated by using algorithms such as rules, parameters assorted data, etc. With the application of L-systems, generative, and fractals techniques, modelers can create highly detailed and realistic models.
Procedural modeling is ideal for VFX, game development, and generating landscapes due to the flexibility of shape determining and scalability.
7. Sculpting (or Digital sculpting)
Digital sculpting in 3D modeling is a digital manipulation technique for shaping up an object. It is similar to pottery work. With the software, users pull, push, smooth, and pinch a flat block (virtual clay) to formulate a structure, adding texture and details until it resembles the original target.
Sculpting is used for highly detailed and refined shapes, such as character design, product design, texturing, 3D printing, etc.
8. BIM (Building Information Modeling)
3D BIM Modeling is the virtual representation of infrastructure projects. With this technology, architects, and engineers build intelligent, 3D models of buildings or other constructions to display the structure, materials, cost information, etc, and thus get collaboration improved, visualization, and efficiency enhanced.
What is the Best 3D Modeling Software?
Among the diverse range of software available in the market, our team shortlisted, compared 20 of them, and boiled down to 5. Check out the list of 5 best 3D modeling software, both free and paid versions.
1. Autodesk 3Ds Max
Autodesk 3Ds Max is a multi-faceted modeling software. It offers pro-level functionalities and has a diverse set of comprehensive tools for high-quality design, visualization, animation, etc. The software is especially popular among interior and architecture designing, gaming and filming, and industries that require intricate details design.
Features
- Retopology tools
- Realistic materials with variants
- Color management and compatibility
- Interactive viewpoints to reduce design iteration
- Supports glTF, USD, FBX, and CAD file formats
| Pros | Cons |
| Diverse tools for complicated design | The system requires a powerful setup |
| Dynamic and customizing interface | |
| Compatible with third-party plugins |
2. Blender
Blender is an open-source 3D creation suite offering an entire pipeline, from modeling to video editing. The tool is perfect for team collaboration, and the offered features are suited both for personal and commercial usage.
Features
- Rendering and modeling
- Sculpting and VFX
- Animation and Rigging
- Pipeline and Simulation
| Pros | Cons |
| Free software for 3D modeling | Doesn’t support NURBS |
| Has versatile tools for different work | |
| A large active community to connect with |
3. Autodesk Maya
Autodesk Maya is one of the best 3D design software. It is equipped with industrial-grade features for modeling, rendering, simulation, character movements, and so on. This is the reason Autodesk Maya is often used in VFX and animation works.
Features
- Modeling and Rigging
- Simulations and Effects (Bifrost)
- Look at the development and rendering
- Pipeline and OpenUSD workflows
| Pros | Cons |
| Industry-level work | The software is costly. |
| Procedural effect | |
| Photoreal rendering |
4. ZBrush
ZBrush is a 3D printing software, renowned in the industry for its detail-oriented working accessibility. It works similarly to Adobe Substance 3D modeler, allowing users to sculpt on clay (virtually).
Features
- Base Mesh Creation and Brush System
- Sculptural Freedom and Polygon Modeling
- Crease Edge UV Unwrap and MorphUV
- Polypaint, SpotLight, and Custom Materials
| Pros | Cons |
| Photorealistic rendering | Steep learning curves |
| Has numerous plugins | |
| Powerful organic sculpting tools |
5. SketchUp
SketchUp is one of the best sketching tools that is versatile, user-friendly, and intuitive. It allows individuals and companies to proceed with their miniature to massive 3D design works. However, the tool is mainly suitable for early-stage designs.
Features
- 2D Drawing
- 3D Imaging
- 3D Design and modeling
- Animation and collaboration tools
| Pros | Cons |
| Easy to use | Lacks photorealistic objects |
| Quick modeling | |
| Integrates with other software |
How to Learn 3D Modeling
To learn 3D product modeling, choose your preferred 3D modeling and rendering software (Maya, Blender, ZBrush, SketchUp, and others), understand the basics of 3D modeling concepts, practice with tutorials, and build a portfolio. Ensure to focus on fundamental shapes, box modeling, and refining details, then try creative works, like texturing, lighting, and rendering.
Step 1: Choose an Easy-to-Understand Software
3D software for product modeling and rendering provides several features and benefits that are compatible for beginner to advanced users. For example,
- Blender: An open-source, versatile option with a large community and extensive online resources.
- Maya: A professional-grade software often used in the animation and gaming industries.
- Autodesk 3DsMax: A feature-rich 3D modeling, rendering, and animation software suitable for product design and visualization.
- ZBrush: A digital sculpting, modeling, and painting software used to create highly detailed 3D models.
- SketchUp: A good choice for architectural and simple object modeling.
all types of features and advantages, for beginner to advanced users. Find one with an industry reputation for an easy interface and beginner-friendly approaches. For example, SketchUp is easy to understand for new learners.
Step 2: Know the Basics and Practice Regularly
Most software provides a guide on how to use it. Check that to learn and practice the fundamentals, such as –
- 3D Modeling Concepts: Familiarize yourself with terms like vertices, edges, faces, polygons, and NURBS.
- Modeling Techniques: Start with box modeling, where you build a 3D object from basic shapes.
- Working with References: Learn to use reference images and sketches to guide your modeling process.
- Basic Shapes: Practice creating objects from primitive shapes like cubes, spheres, and cylinders.
- Refining Shapes: Learn to manipulate vertices, edges, and faces to create more complex forms.
- Topology: Understand how the structure of your model affects its appearance and how to optimize it.
- Texturing: Apply colors, materials, and textures to your 3D models to make them look realistic.
- Lighting and Rendering: Learn how to use lighting and rendering techniques to enhance your models.
Step 3: Utilize Online Resources
Explore popular and resourceful YouTube channels, like Blender Guru or CG Cookie, for step-by-step tutorials. Or, you can go with online courses, like Udemy, Coursera, and others, for structured processes on 3D modeling.
Step 4: Practice and Experiment
Maintain regularity, don’t be afraid to experiment and find out what works best for you, build a portfolio to showcase your skills, join 3D modelers’ online communities to get feedback and experiences, and try to participate in 3D modeling contests.
Step 5: Stay Updated
Research 3D product modeling trends and specific techniques for different products, i.e., apparel, industrial design, or others. If possible, collaborate with other designers or artists to create more complex product visualizations.
What are the Best Online Courses for 3D Modeling?
The 5 best online courses for 3D modeling are Lynda, Autodesk, Udemy, 3DTraining, and Coursera. These 3D modeling programs are helpful for beginners to advanced levels.
| Platform | Why to Choose | How to Get Started |
|---|---|---|
1. Lynda | Lynda is the online learning platform that LinkedIn offers. There are a variety of training courses to teach you simple shape intricating detail designing, polygonal modeling, and topology. You can learn about the usage of different industry-grade 3D software to acquire skills in high-quality models. | Download the Lynda app and log in with your LinkedIn ID. |
2. Autodesk | Autodesk is updating its learning resources with on-demand courses to help build 3D modeling skills. Learners will find tutorials and curated lists, hone skills from the core, and get ready to march forward in their careers. | Sign in to start learning. |
3. Udemy | Udemy is one of the popular e-learning and skill development platforms. From software to technique, Udemy has all types of courses available for beginners to advanced learners. So, you will find a wide variety of courses by industry experts within your budget. | Sign in to access both free and paid courses. |
4. 3DTraining | 3D training is an offering of interactive training programs to help enthusiast hone their skills. Apart from the course materials, the platform offers live support and guidelines directly from industry professionals and assigns learners to different on-demand projects with deadlines. So, students improve their skills. | Sign in with their website. |
5. Coursera | Similar to Udemy, Coursera offers diverse 3D skill development specialized courses. It offers high-quality content from industry experts, assisting learners in their professional journey by expanding their knowledge into industry insights. | Create an account with Coursera to access free courses. |
What Kind of Computer Do You Need for 3D Modeling?
You’ll need a computer with a powerful processor (CPU), a high-quality monitor with good color accuracy, a dedicated graphics card (GPU), 32GB or more RAM, and a fast NVMe SSD for smooth functionality for 3D modeling. Below, we’ve discussed in detail:
- CPU: A high-core-count processor (i.e., AMD Ryzen 9 or Intel Core i7/i9 processors) is crucial for handling complex scenes and rendering tasks.
- GPU: A dedicated graphics card with ample VRAM (video RAM) (i.e., NVIDIA GeForce RTX, Quadro series, or AMD Radeon Pro series) is essential for real-time rendering and smooth performance.
- RAM: As mentioned earlier, 32GB of RAM is recommended for heavy 3D modeling tasks and a smooth workflow. However, you can use 16GB for basic modeling and simpler scenes, but you’ll face difficulties with more detailed and resource-intensive projects. 64GB RAM is ideal for large and complex scenes, animations, and architectural visualizations. 128GB RAM for luxury product items with complex simulations.
- Storage: A fast NVMe SSD with a large-capacity HDD is ideal for the operating system and frequently used applications.
- Monitor: A high-quality monitor with good color accuracy is essential for visualizing your 3D models accurately.
- Operating system: Most 3D product modeling experts prefer Windows, but Macs are also used.
- Workstations: HP Z series workstations (i.e., Z4, Z6) and Dell Precision series are designed for professional use and offer powerful performance for 3D modeling and rendering.
- Laptops: For portable flexibility, use laptops like the ASUS ProArt series, Dell Precision 7780, or the HP OMEN Transcend 14.
Before choosing the best computer for your 3D product modeling projects, consider your project details and the 3D modeling software you use.
What are the Best Drawing Tablets for 3D Modeling?
The 3 best drawing tablets for 3D modeling are: Wacom Intuos Pro, Wacom Cintiq Pro 16, and Huion Kamvas Pro 16 (2.5K QHD). For more details, check out below:
1. Wacom Intuos Pro
The tablet is a classic choice for professional 3D modelers, sculptors, and texture artists for its exceptional performance in a sleek package. Its pressure sensitivity (8192 levels), tilt support, and customizable ExpressKeys make it an all-around powerhouse.
Key features
- Multi-touch gestures for intuitive navigation
- Available in small, medium, and large sizes
- Wireless connectivity for clutter-free setups
- Ergonomic Pro Pen 2 feels natural and enhances creativity
- Ultra-thin, matte black, minimalistic design
Best For: Professionals who prefer non-display tablets for sculpting, modeling, and portability with Wacom reliability.
2. Wacom Cintiq Pro 16
Wacom Cintiq Pro 16 is a powerful, versatile pen display that comes in a variety of sizes. Whether you want to keep things efficient at the 16” size or need tons of space for major projects at the full 27” size, this one is the best choice for you.
Key Features
- USB-C and HDMI connectivity
- 4K UHD touchscreen display (3840×2160)
- EMR technology (battery-free pen) ensures long-term use
- Trusted by professionals in animation, gaming, and product design
- Sleek, premium aluminum and matte finish design
Best For: Professionals seeking ultimate precision, brand reliability, and stunning visual clarity for 3D sculpting, texturing, and modeling.
3. Huion Kamvas Pro 16 (2.5K QHD)
2.5 K QHD resolution and a 15.8-inch IPS screen provide dinner images at a time. Also, its 186PPI highlights all details to look clearer on this pen display. With this drawing tablet, you can combine the antiglare glass and the screen.
Key Features
- 2.5K QHD laminated display (2560×1440)
- USB-C connection with anti-glare glass
- Modern, slim, minimalist design with a professional aesthetic
- Battery-free stylus with durable nibs
- Solid build quality with a metal back panel for strength
Best For: Intermediate to professional users wanting high resolution, durability, and value without Wacom’s high price tag.
How Long Does it Take to Learn 3D Modeling?
Learning the basics of 3D modeling can take 6 months, but mastering this skill as a professional can take years, depending on your consistent practice, dedication, the complex functionalities you aim to learn, and the software used. Though there are no fixed rules, the time frame is completely dependent on individuals’ learning speed, software complexity, and practice. However, we’ve highlighted a common time frame below:
| Time Schedule | Techniques & Software |
|---|---|
| Basic 3D modeling skills (1-3 months) | Learning basic software tools (Blender, Maya, 3Ds Max), creating simple objects, understanding the interface, and basic rendering. Ideal for beginners aiming to create basic models for visualization. |
| Intermediate for projects (3-6) | Developing clean topology, working with modifiers, UV unwrapping, texturing, and creating simple animations or product visualizations. Suitable for freelancers and design professionals expanding services. |
| Professional 3D techniques (6months-Years) | Mastering complex organic and hard-surface modeling, photorealistic texturing, advanced rendering, rigging, and industry-standard workflows. Required for careers in gaming, VFX, product modeling, AR/VR, or architectural visualization. |
How to Make 3D Product Models
To create a 3D product model sample image collection to create a basic 3D shape, select software (e.g., Blender) to refine details, create a basic shape, UV unwrapping or unwrapping UV, add texture, and export texture.
Step 1: Sample Image Collection
First, we need to collect reference images for the model we want to create.

Step 2: Choose DCC Software
Set up reference images in Digital Content Creation (DCC) software. Here we’ll use Blender to proceed with our work.
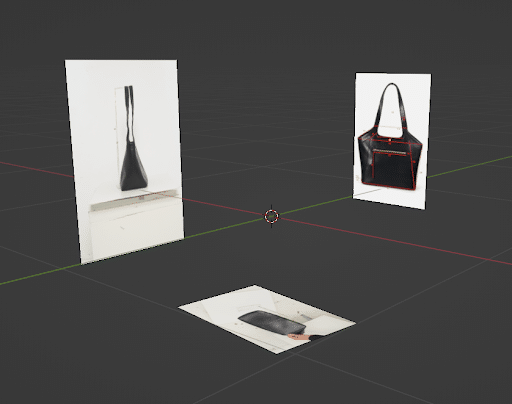
Step 3: Create a Basic Shape
In this step, we need to create a basic shape. As you can see, we have placed the necessary images to generate the outline of the bag.
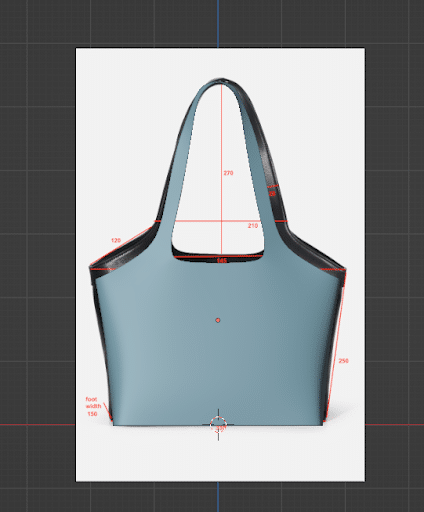

Step 4: Add Details
Once we’re satisfied with the basic shape then, we’ll start adding details measurements, size, etc.
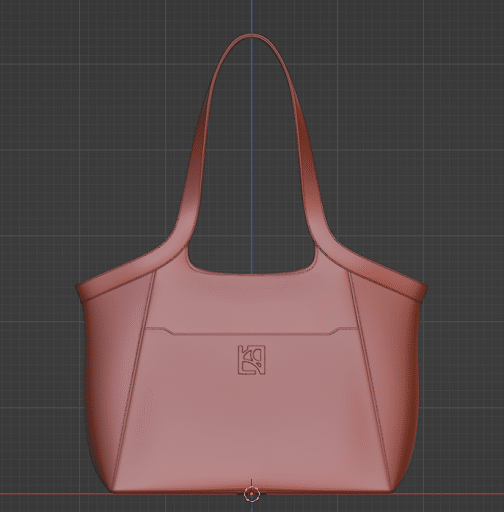
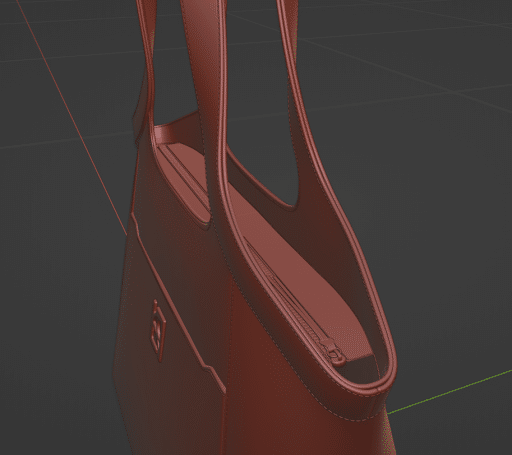
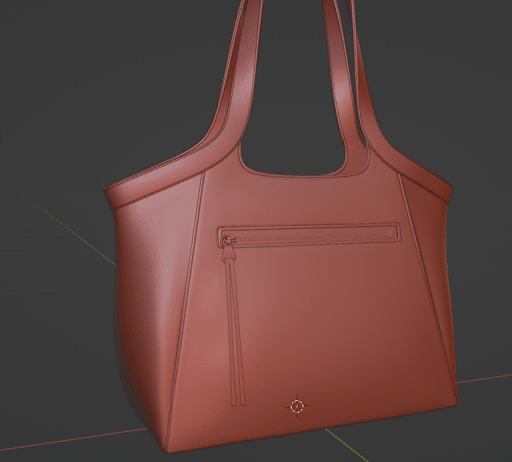



Step 5: Unwrap UV
With this process, we will cut the seams to flatten the mesh and create an organic shape. It will bring the realistic visual of the 3D model.

Step 6: Add Texture
Now we’ll create textures for this bag. Here we will use Adobe Substance Painter 3D.
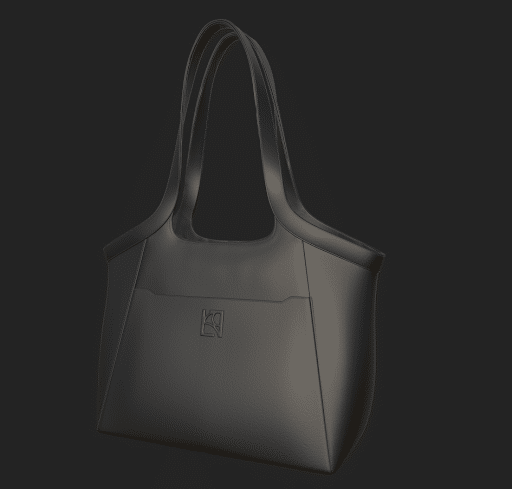

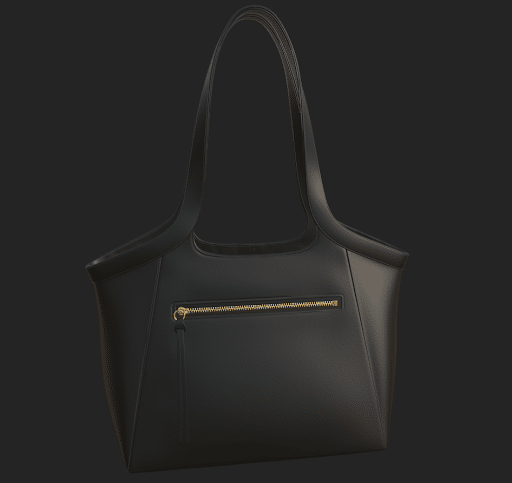
Step 7: Export Texture
Now we’ll export textures and implement them into the model. There you have it, the 3D modeling
What File Formats are Used in 3D Product Modeling?
Some common 3D product modeling file formats are OBJ, FBX, STL, STEP, GLTF/GLB, COLLADA, 3DS, and AMF. These file formats vary in their capabilities and specific tasks. For example, STL and AMF are popular choices for 3D printing, whereas FBX and COLLADA are used for data exchange. Other benefits of different 3D product modeling and rendering are highlighted below:
| File Format | Best for | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| OBJ (.obj) – Object File | General modeling (geometry, textures), games | Universal, lightweight, easy to use |
| FBX (.fbx) – Filmbox | Animation, VFX, games | Rich data, animation support, interoperability |
| STL (.stl) – Stereolithography | 3D printing | Simple, robust, printer-compatible |
| 3MF (3D Manufacturing Format) | Advanced 3D printing | Modern supports full print data |
| STEP – Standard for the Exchange of Product Data | ACAD, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing | Precise, cross-CAD compatible |
| GLTF/GLB (.gltf/ .glb) – GL Transmission Format | Web, AR/VR, real-time | Fast, small, web-optimized, PBR support |
| COLLADA (COLLAborative Design Activity) | AR/VR workflows, animation, game development | Interchangeability across 3D apps and platforms |
| AMF (Additive Manufacturing File) | Product design, architecture, and medical technology | Flexible and supporting features like color, materials, and textures |
Can Small Businesses Benefit from 3D Product Modeling?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from 3D product modeling, such as e-commerce and retail businesses, product design and manufacturing startups, home decor, jewelry retailers, tech gadgets, and more. How do these small businesses benefit from 3D product modeling? The key reasons are as follows:
| Small Business Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| E-commerce & Retail | Interactive product views, easy updates, cost-effective visuals |
| Product design startups | Rapid prototyping, faster iterations, and clear communication |
| Fashion & Apparel | Texture detail, virtual try-ons, engaging online experience |
| Home decor & Furniture | Customization, AR visualization, interactive catalogs |
| Jewelry & luxury goods | High-fidelity detail, virtual tours, quality emphasis |
| Tech Gadgets & Electronics | Feature demos, prototype cost reduction |
Where to Outsource 3D Modeling Service?
You can outsource the 3D modeling service and rendering service from a top-rated agency or hire freelancers from popular freelancing platforms. However, for fast solutions, quality work, services-on-demand, 24/7 availability, and cost-effective solutions, it’s a wise decision to outsource to a 3D modeling service provider, like Clipping Path Studio. Below, we’ve highlighted the key features of these 2 platforms and picked a suitable one that aligns perfectly with your business:
1. 3D Modeling Agency
Authentic 3D modeling service providers have a reliable in-house team. The members have diverse skill sets and are technologically advanced to meet the unique needs of clients.
When to choose a 3D Modeling Agency?
- Have high-volume, intricate, and complex projects.
- Looking for VR, architectural, and gaming-specific category services
- Need to ensure high-quality, & precise work from industry experts
- Have a tight schedule to comply with marketing approaches
- The in-house team has a lot to deal with
Budget: Average pricing starts at $500 and varies based on projects. Agencies range from boutique to large full-service categories. You will always find companies that offer budget-friendly solutions.

2. Freelance Platform
The freelancing platform is an affordable place to find all types of work from all levels of workers. Omitting the risks, you can get quality work to meet your target. Some popular freelancing platforms are Fiverr, Upwork, Upwork, People Per Hour, etc.
When to choose freelancing platforms?
- Flexible work schedules
- On a tight budget
- Need the fastest work
Budget: Starts from as low as $10 to as high as.
How Much Does 3D Product Modeling Cost?
3D product modeling costs range from $50 for simple models to $5K+ or more for complex, high-detail designs. The industry-specific 3D modeling costs are as follows:
- Product prototyping and design costs range from $200 to $2,500 or more, depending on functionality and material simulation.
- Real estate 3D models range from $1,000 to more, depending on the external model, an interior layout, or a full property blueprint.
- Gaming characters can cost between $425 for basic assets and $10,000 or more for high-detail models for animation.
Below, we’ve highlighted a detailed pricing table based on 3D model complexity, 3D work details, and artist expertise.
| 3D Model Complexity | Work Details | Appx. Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Simple | Partly organic shape or super-detailed (e.g., highly detailed characters, complex machinery) with a highly complex structure. | <$150+ |
| Medium | Detailed or simple organic shape (e.g., furniture, basic characters) with simple texture and some complex PBR material. | <$1000+ |
| High | Partly organic shape or super-detailed (e.g., highly detailed characters, complex machinery) with a highly complex structure . | <$2500+ |
Other pricing strategies are listed below:
- 3D per model pricing structure works well for single or standalone projects, for example, creating one character or a specific product prototype.
- 3D projects’ hourly rate ranges from $20 to $200 or more, based on the 3D artist’s expertise.
- The monthly rate for 3D modeling costs between $300-$450+ per month, depending on the outsourced company and the client’s requirements.
- Project-based rates offer a flexible packaging deal, making budgets easier for larger, more complex projects. For example, marketing campaign visuals may cost $3,000-$10,500 or more for a complete set of models. Whereas, interactive game environment design will cost $15,000+ or more.
Different factors that influence 3D product modeling cost:
- Expertise-level: Industry-expert 3D modelers charge higher than freelancers due to years of marketplace experience and high-quality work.
- Software used: Some 3D software requires licenses that impact overall costs (e.g., AutoCAD – $210/month, Blender – Free).
- Project types and complexity: Complex projects like interior design, jewelry products, or others cost more than simpler ones.
- Turnaround Time: Expedited projects incur additional fees.
- Post-Production: Revisions may add 10-20% to the project cost.
- Regional: Cost varies depending on the region (labor costs and economic conditions). For example, an upscale model may cost $1,000 in the U.S., but it could be $400 in India or Eastern Europe (approx value).