Color correction in video editing is the first step to fix color, exposure, and white balance so the footage looks natural. Color grading is the step of setting the mood, tone, and cinematic style, which comes after the color correction process.
Correcting a video is necessary mainly for fixing flaws, ensuring accuracy, adjusting the appearance to a natural level, and making the footage suitable for applying grading. After a video is professionally corrected, application of grading ensures sentimental, creative, theme-based videos to fulfill commercial goals.
What you’ll learn in this article
- 1 Color Correction vs Color Grading in Video: Definition
- 2 Color Correction vs Color Grading: What’s the Key Difference?
- 3 Color Correction vs Color Grading in Video: When to Use?
- 4 Color Correction vs Color Grading in Video: Uses of LUTs
- 5 Color Correction vs Color Grading: Terms and Tools
- 6 Color Correction vs Color Grading: Cost
- 7 How Do You Color Correct a Video?
- 8 How Do You Color-Grade a Video?
- 9 FAQ’s
Color Correction vs Color Grading in Video: Definition
Color correction is the basic application, and color grading is the final, creative, and artistic application of color. Correction works as the base for grading to create professionally colorized videos.
What is Color Correction in Video Editing?
Color correction in video editing is the video processing process of fixing and adjusting existing colors, hues, tones, and shades in the raw footage and transforming it towards a natural, consistent, and true-to-life appearance across all scenes. Professionally corrected color ensures high-quality, consistent visuals and authenticity in videos.
Color correction is a set of changes to balance colors, which includes different techniques as follows.
- White balance adjustment for refining color temperature.
- Exposure and brightness correction for balancing light levels.
- Scopes & waveform monitoring for precise color balancing.
- Contrast and saturation to adjust highlights, shadows, and color intensity.
- Primary and secondary color correction to adjust global color (primary) or specific colors (secondary).
What is Color Grading in Video Editing?
Color grading is an advanced level color application during the video editing segment for creatively adjusting colors, tones, moods to create a cinematic style or emotional theme to finalize the purpose of the story narrative. The application of color grading strengthens the story’s plot and creates visually appealing scenes to fulfill commercial purposes.
There are many ways to color grade a video that video editors use, which are as follows.
- LUTs (Look-Up Tables) for preset color styles.
- Curves adjustment to fine-tune the brightness, contrast, and color channels.
- Secondary color correction to swap colors or isolate objects.
- Gradient masks & power windows for changing color to specific areas.
- Color wheels to apply shadows, midtones, and highlights for mood and depth.
- Film emulation & presets for simulating the look of classic film stocks.
Color Correction vs Color Grading: What’s the Key Difference?
The difference between color correction and color grading is that color correction is the first step of color adjustment that fixes color issues to make a video look natural and real-life-like, while color grading is the final adjustment segment of color used for adding mood, tone, and visual style to match the story’s emotion and atmosphere.
Other differences between color correction and color grading are as follows.
| Criteria | Color Correction in Video | Color Grading in Video |
|---|---|---|
| Actions | Fixes color and exposure issues for an authentic and natural look | Improves the video’s mood, tone, and style for storytelling |
| Emphasis | Ensuring accurate and balanced color appearance | Creating aesthetic and thought-provoking color effects |
| Workflow | First to apply for creating clean footage | Applied after correction to stylize the videos for the final output |
| Required tools | Calibrated monitors, scopes, exposure, white balance sliders, etc | LUTs, color wheels, curves, creative filters, etc |
| Example | Model skin tone fixing | Warm and cinematic morning hour creating |
Table: Differences between color correction and color grading in video
Color Correction vs Color Grading in Video: When to Use?
There are certain situations when you need to apply color correction, and in other cases, color grading. A common ground is that all pictures that need color grading must have color corrected first. The situations where you correct or grade your photos are as follows.
When to use color correction:
- During uneven lighting to too dark, or too bright scenarios.
- Adjusting the incorrect white balance to balance unnatural blue, orange, or green tints.
- Sequencing mismatched footage and matching colors across multiple cameras or lenses.
- Fixing skin tones to ensure natural and realistic skin colors.
- Rectifying images’ technical errors to adjust overexposure, underexposure, color casts, etc.
When to use color grading:
- Setting the right mood or theme for creating warmth, drama, or suspense aids the story development.
- Creating a cinematic appearance for a filmy style and professional output.
- Emphasizing the narrative moments, purposes with color tone shifts.
- Following brand consistency to align visuals with the project style.
- Stylize scenes to make them more memorable.
Color Correction vs Color Grading in Video: Uses of LUTs
Use of LUTs in color correction and color grading saves time, enhances color, and maintains consistency. Look-Up-Table or LUT in video editing is a preset color filter for changing colors in a video. As it is a non-destructive working process, video editors can retain original footage while the LUT applies changes, which include adjusting gamma, saturation, luminance, contrast, and hue across the video footage.
It can be applied to LOG, RAW, Rec. 709, Rec. 2020, and HDR footage. LUTs can also be imported as packs for instant application to create a certain look across all clips. There are 6 types of LUTs used in video editing as follows.
| Types of LUTs | Use Cases |
|---|---|
| 1. Transformation LUTs | Convert footage from one color space to another. |
| 2. Viewing LUTs | Help users preview colors on set, rectifying the muted or washed-out images. |
| 3. Calibration LUTs | Ensure uniform colors throughout the editing workflow. |
| 4. Log Normalization LUTs | Tone-map LOG footage to Rec. 709, DCI-P3, or HDR color spaces. |
| 5. 1D LUTs | Adjust a single parameter or overall contrast uniformly. |
| 6. 3D LUTs | Control hue, saturation, luminance, gamma, and contrast separately in 3D color space for more precision. |
Table: Types of LUTs in video editing
Color Correction vs Color Grading: Terms and Tools
There are several terms and tools used in video editing; some of the frequently used terms include color, video color (RGB), color wheels, color curves, HSL (hue, saturation, and luminance), HDR, color sliders, exposure sliders, white balance tool, calibrated video monitor, LUTs, and video scopes.
- Color
Color is our brain’s processing of interpreting light that triggers our emotions and moods. The wavelengths of light make color appear differently. The imbalance of colors in the video makes it look unnatural, and breaks the intention of the narrative and story flow.
- Video Color (RGB)
Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) create the video color. All the colors we see are derived from the mixture of these three colors. The right use of RGB determines the warmth, coolness, or vividness of the color appearance on the screen.
- Color Wheels
Color wheels are a circle of colors with a point. Moving It allows you to adjust shadows, midtones, and highlights in the video so you can create a warm or cool tone. Or you can adjust the tones, apply a quick color effect to fulfill the narrative purposes.
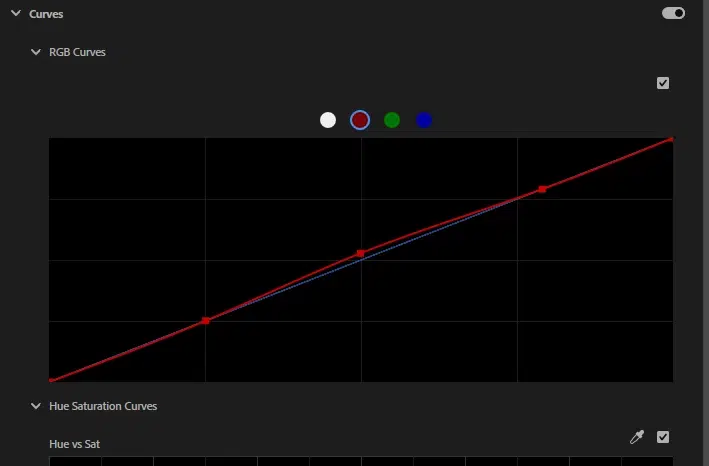
- Color Curves
Color curves allow precise control over tone and brightness. You can darken or brighten any specific parts, adjust shadows and midtones, and tweak RGB levels for controlling contrast and color detail.
- Hue, Saturation, and Luminance (HSL)
In the color theory, hue is the main color, saturation is the color intensity, and luminance is the brightness level. Adjusting HSL allows you to create the scenery natural, balanced, or dramatic and bold as per your requirements.
- HDR
HDR or High Dynamic Range displays more detail in both bright and dark parts of a video. Use of HDR makes rich color, clear highlights, and deep shadows, which contribute to creating more natural and life like images, as human eyes see.
- Color Sliders
Color sliders are the tool to fine-tune RGB colors and brightness values. Both color wheels and color sliders work similarly, but color sliders allow you to work on individual channels.
- Exposure Slider
The exposure slider balances the overall brightness or darkness of the images. Exposure correction ensures editing both shadow and highlights, which results in creating a balanced and detail-clear visual foundation, effective for color grading.
- White Balance Tool
The white balance tool works on color temperature and eliminates unwanted blue, orange, or green tints from lighting. As a result, the white looks true white, black appears real black, and so do other colors.
- Calibrated Video Monitor
A calibrated monitor is used for video editing to view true colors. Uncalibrated monitors or screens might lack showing brightness or tones to the fullest. Professional video editors calibrate their monitors or color bars so that they can ensure consistent and accurate colors.
- LUTs (Look-Up Tables)
LUTs are preset color styles that video editors use for creating a specific tone, feel, or look. Using loot saves time and lets users maintain a consistent color presentation across the video footage.
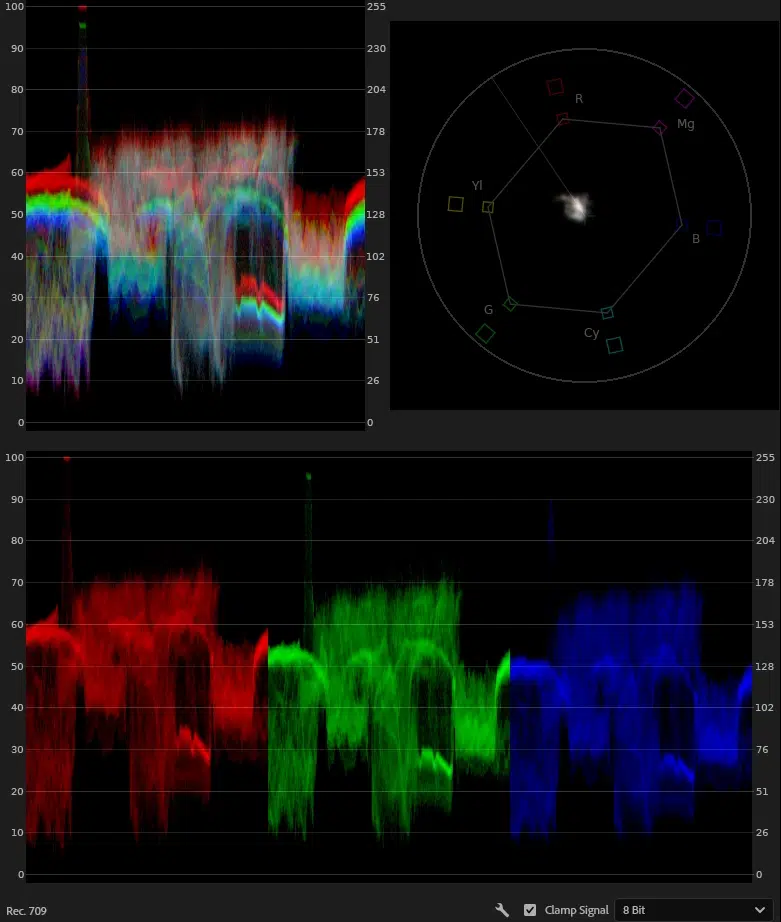
- Video Scopes
Video scopes such as Waveform, Histogram, and Vectorscope show color and brightness data and allow users to check exposure, contrast, and color balance. These scopes are essential for creating a consistent and professional-grade application of color correction and color grading.
Color Correction vs Color Grading: Cost
The cost of color correcting a 1-minute video starts at $40. The cost of color grading a 1-minute video starts around $50. The cost of corrected or graded video is calculated based on various factors, such as video editors’ expertise, location, type of service providers (agency or individual editor), video length and purposes, editing complexity, turnaround, and number of revisions. Also, the price varies per-project, per-minute, per-hour, or monthly basis.
How Do You Color Correct a Video?
Color correcting a video is an advanced-level task, and that’s why most e-commerce businesses, industries, companies, advertising and marketing agencies, and media and film organizations hire professionals to polish their footage. As part of professional video editing effects, color correction enhances visual consistency, improves mood, and strengthens brand identity. You can color correct a video using video editing software by following these steps.
Step 1: Open the File
Import your raw videos into a video editing software such as Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, or Final Cut Pro and place the clips on your timeline to start editing on individual scenes.
Step 2: Adjust White Balance
Adjust the level of white balance to fix the color temperature and tint to ensure the white appears naturally white and there are no unnecessary color casts.
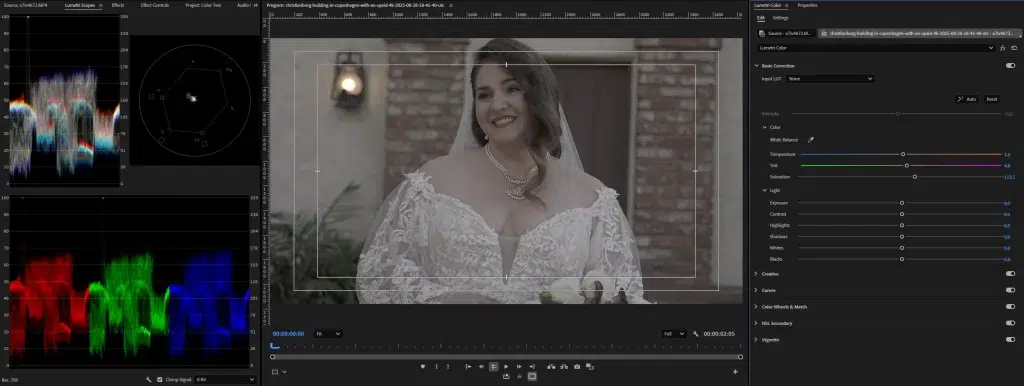
Step 3: Correct Exposure and Contrast
To correct the contrast and exposure in the footage, balance its brightness, shadows, and highlights. This step will ensure recovering lost details in the dark areas so that the footage appears clean and professional.
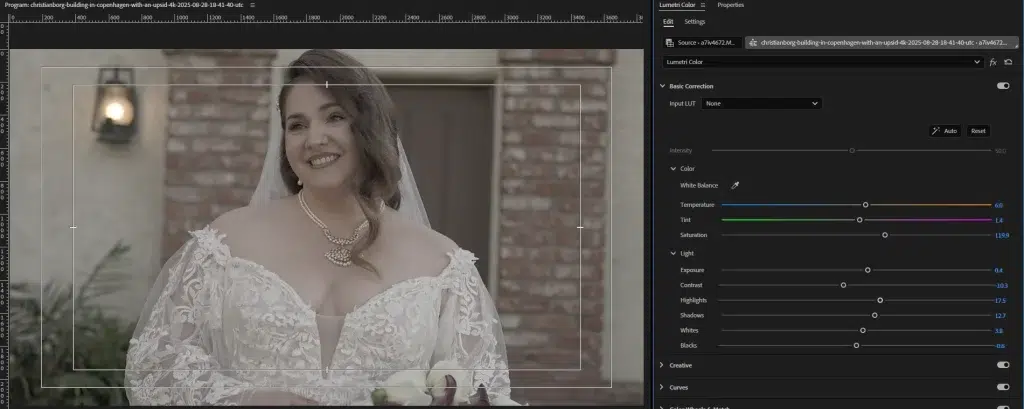
Step 4: Fine-tune Colors and Skin Tones
Adjust hues and saturation through color wheels or curves. Balance skin tones to make them appear natural.

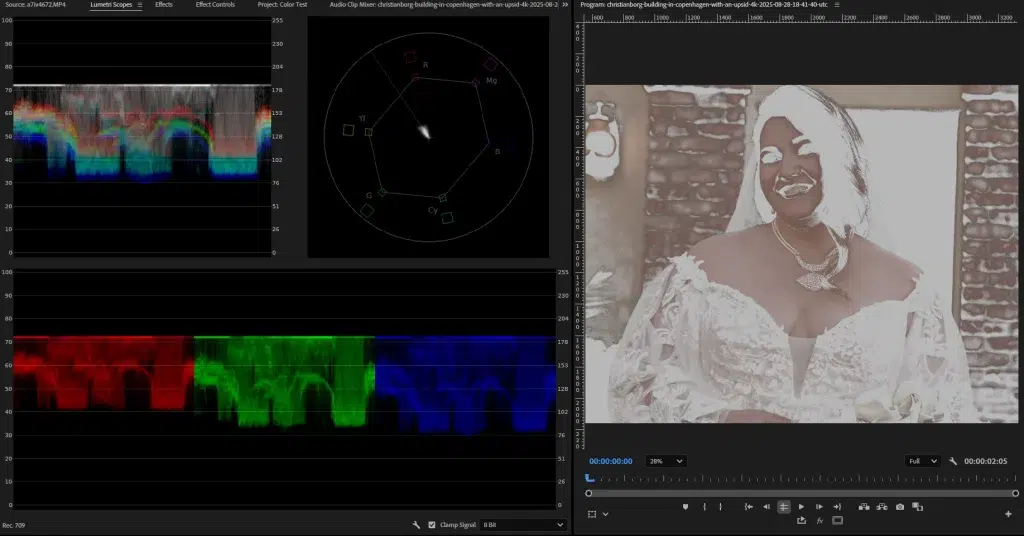
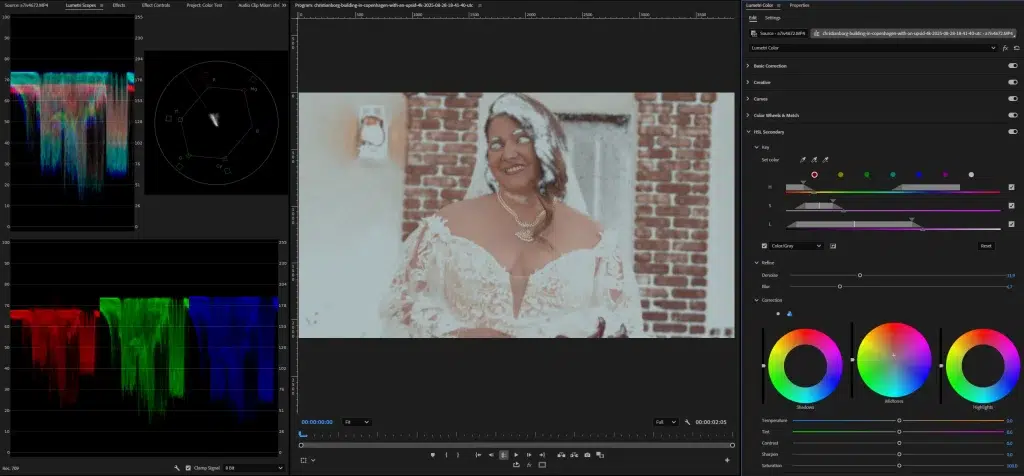
Step 5: Check and Export
Verify the accuracy through the RGB parade and Vectorscope tools. If everything looks fine, export the video for grading and final editing.
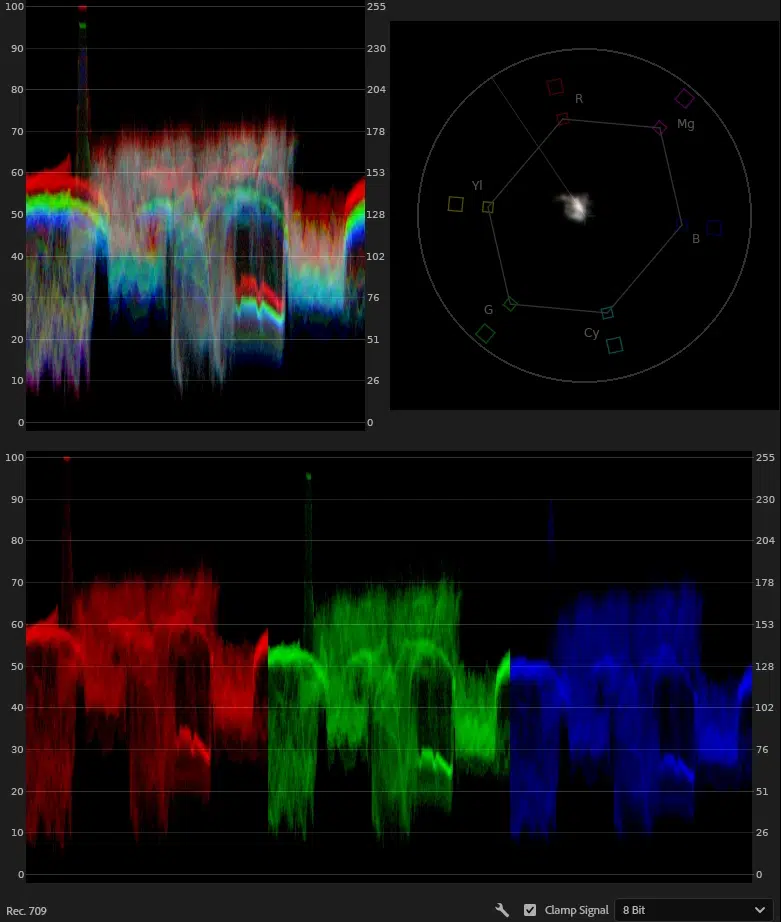
How Do You Color-Grade a Video?
Here is a step-by-step guide to color-grading a video to create professional results.
Step 1: Take Your Color-corrected Video
Upload your color-corrected videos; those videos will lay the groundwork to perform color grading in the video.
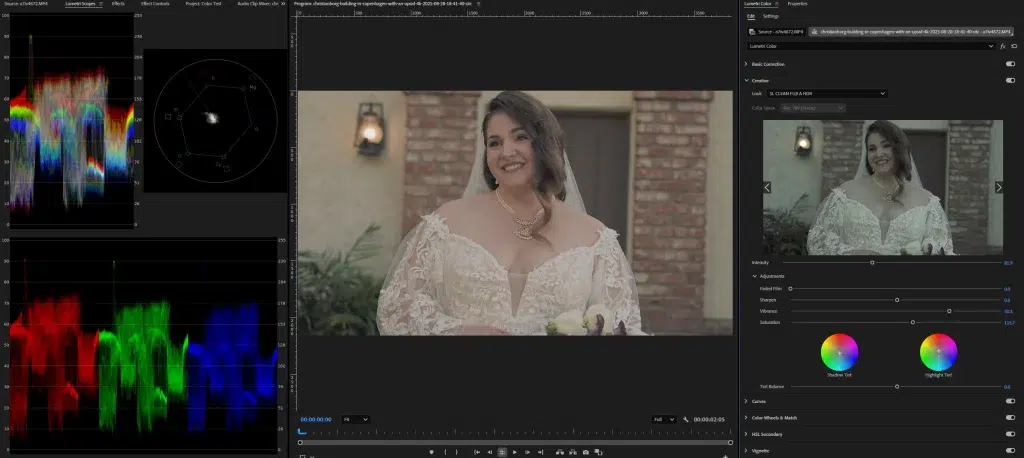
Step 2: Choose a Look, Theme, or Mood and Use LUTs
Depending on your purpose, decide the video’s theme, look, or mood; this will be the base for grading colors. Now, apply a LUT (Look-Up Table) or preset for matching purposes; this is the fastest way to give videos a quick and consistent style. Once you have applied LUTs or presets, adjust the intensity for a natural and authentic look.
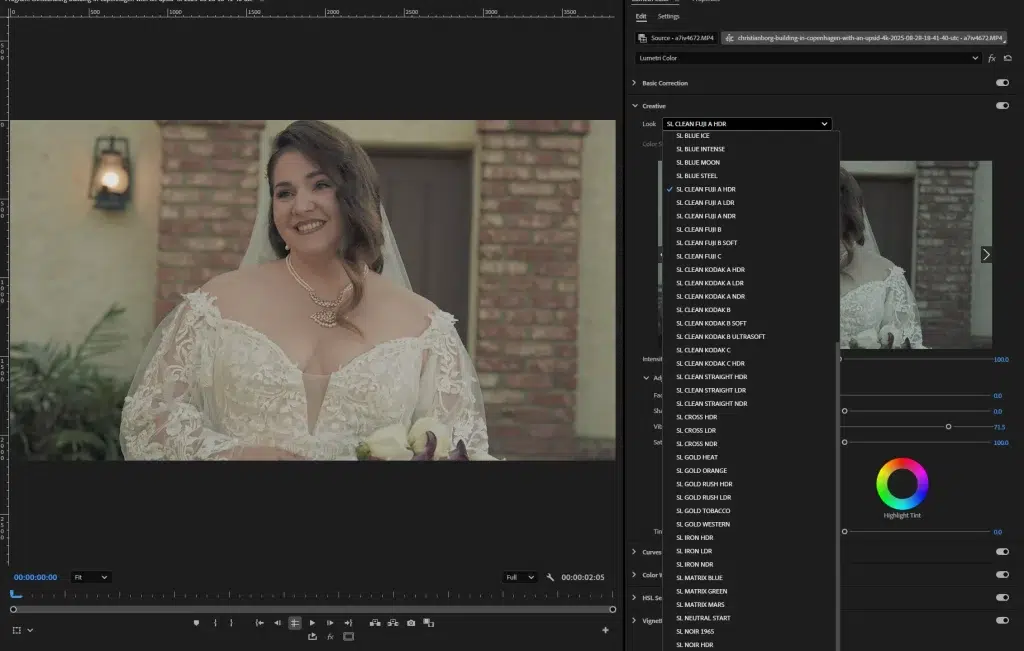
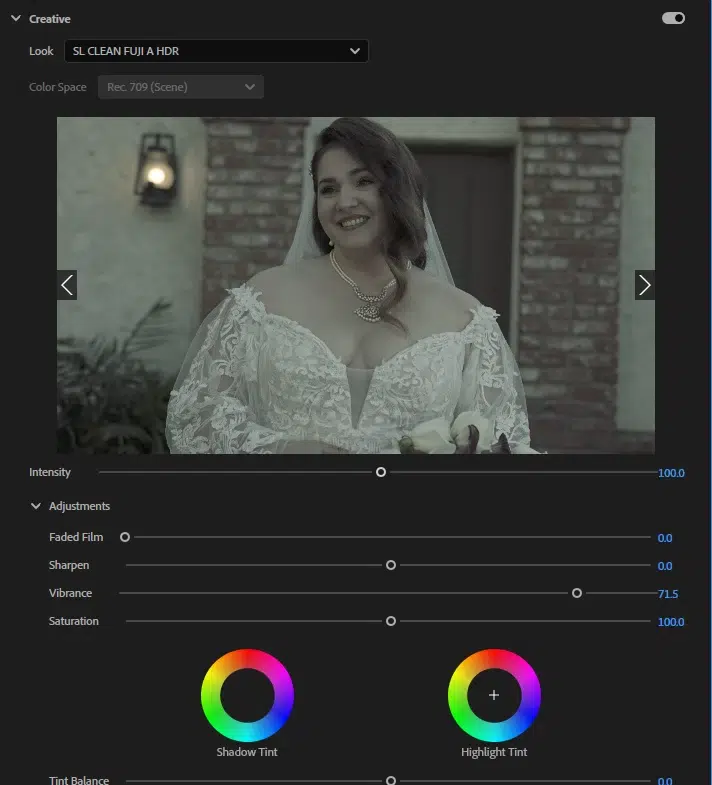
Step 3: Adjust Color Wheels and Curves
Fine-tune shadows, midtones, and highlights using color wheels or simple sliders. Adjust small changes to make the videos cohesive and visually striking.

Step 4: Match Shots and Export
Balance all the tones across the video. When every scene looks smooth and professional, your video is color graded and ready to export.
FAQ’s
Is color correction the same as color grading?
No, color correction and color grading aren’t the same, even though both work on the adjustment of colors. Color correction is the fixing of colors, exposure, white balance, hue, and tone to create natural-looking videos, making the base for color grading. Color grading is the creative application of colors on the corrected video to set the right mood, theme, and style to create a specific feeling or thought.
Should i color correct before color grading?
Yes, you should apply color correction followed by color grading during video editing. Correction ensures your footage’s natural and balanced appearance, along with inconsistency removal. Then apply creative grading in the videos for specific styles, moods, or a cinematic finish.
Should i color grade my videos?
Yes, you should color grade your videos if you want to make a creative, thoughtful, and professional appearance and evoke viewers’ emotions. Color grading enhances narratives’ storytelling and creates a cinematic vibe.
What is the color hue?
Color hue is the actual color that defines color’s identity or color as the human eye perceives, such as red, green, blue, or yellow. It is the purest color form without any variations such as lightness, brightness, etc. For example, blue and purple share the same hue.
What is color saturation?
Color saturation is the intensity or the amount of hue’s presence in the color. High saturation makes color vibrant, rich, and bold. Low saturation makes color look dull, grayish, and faded. Balancing saturation helps set the right mood in the video’s presentation.
What is color brightness?
Color brightness, also called luminance or value, is the lightness or darkness of a color’s appearance. If the brightness increases, it makes the scene lively, clear, as if there is white mixed in the color, lowering its depth. Whereas, if the brightness decreases, it makes the scene dark as if there is a black mix in it.
Which coloring tools should i use?
You can use several coloring tools such as Lumetri Color (Premiere Pro), Color Wheels and Curves (DaVinci Resolve), or Final Cut Pro’s Color Board. With the assistance of these tools, you can adjust brightness, white balance, contrast, and creative color tones to set the right creative appearance in videos.

