Video sound effects refer to a piece of audio that makes sense with videos but hardly has its own meaning. Video SFX highlights the video content, connects viewers with the scene, and makes them understand the message. Movies, dramas, social media content, music videos, animations, and all types of videos contain high-quality sound effects.
There are 20 types of sound effects categorized based on origin, use, source, including non-verbal, crowd sound, spot sound, off-screen, foley, and isolated sound effects. Platforms like Pixabay, Freesound, Premium Beat, and Envato Elements are some popular SFX libraries that offer different types of audio in free and paid versions. These sounds are available in MP3, AAC, OGG Vorbis, FLAC, ALAC, M4A, WAV, etc formats.
What you’ll learn in this article
- 1 What are Video Sound Effects?
- 2 What are the Different Types of Video Sound Effects?
- 2.1 1. Non-verbal Sound Effect
- 2.2 2. Crowd Sound Effects
- 2.3 3. Spot Sound Effect
- 2.4 4. Off-Screen SFX
- 2.5 5. Foley Sound Effects
- 2.6 6. Isolated Sound
- 2.7 7. Location SFX
- 2.8 8. Environmental/Atmospheric Sound Effect
- 2.9 9. Background Sound
- 2.10 10. Movie Sound Effect
- 2.11 11. Scary Sound Effect
- 2.12 12. War Sound Effect
- 2.13 13. Vehicle-Based Sound
- 2.14 14. Accident Sound Effect
- 2.15 15. User Interface Sound Effect
- 2.16 16. Cartoon Sound Effect
- 2.17 17. Trailer Sound Effect
- 2.18 18. Glitch Sound Effect
- 2.19 19. Custom Design SFX
- 2.20 20. Swoosh/Whoosh/Swish Sound Effects
- 3 Why are Video Sound Effects Important in Video Editing?
- 4 How to Add Sound Effects to a Video?
- 5 How to Adjust the Volume Level on a Video?
- 6 What File Formats are Commonly Used for Video Sound Effects?
- 6.1 1. MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer III)
- 6.2 2. AAC (Advanced Audio Coding)
- 6.3 3. OGG Vorbis
- 6.4 4. FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec)
- 6.5 5. ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec)
- 6.6 6. M4A (MPEG-4 Part 14)
- 6.7 7. WAV (Waveform Audio File)
- 6.8 8. AIFF (Audio Interchange File Format)
- 6.9 9. DSD (Direct Stream Digital)
- 6.10 10. PCM (Pulse-Code Modulation)
- 7 Where to Download Royalty-free Video Sound Effects?
- 8 How to Choose the Right Video Sound Effects
- 9 What are the Best Video Sound Effects Examples?
What are Video Sound Effects?
Video sound effects (SFX) are the artificial auditory elements used in video to create realism and add depth to appeal to viewers’ emotions. Video SFX mimics the sounds that come from daily life activities, both living and non-living objects. The purpose of using VFX in videos is to add immersion, enhance reality, and connect viewers with the visual message.
What is the Difference Between Sound Effects and Sound FX?
The difference between sound effects and sound FX is the abbreviation. Sound FX is the abbreviated format for sound effects. Effects are the transformation or transition techniques applied both in audio and video. SFX is for sound, and VFX is for video.
Sound effects enhance viewers’ engagement by hypnotizing them. The appropriate use of sound appeals to viewers’ emotions, evoking feelings of happiness, elation, excitement, anxiety, worry, fear, or sadness. Audio makes visuals engaging and sensible, thus keeping viewers invested in the scenario or narrative.
What’s the Difference Between Background Music and Video Sound Effects?
The difference between background music (BGM) and video sound effects is their duration and purpose.
- Duration: Background music in videos lasts longer alongside the existing scenes, whereas SFX in videos are sudden and short.
- Purpose: SFX introduces a specific scene, action, or emotion; background music conveys the right mood.
Other differences between background music (BGM) and video sound effects(SFX) are as follows.
| Parameters | Background Music (BGM) | Video Sound Effects (SFX) |
|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Lower volume than dialogue. | Volume differs from high to low depending on the purpose. |
| Priority | Highlights the overall perception. | Emphasizes a specific action, motion, or detail. |
| Duration | Continuous and long. | Brief and event-specific. |
| Nature of Sound | Sounds melodic. | Sounds specific, or sudden. |
| Affect | Establishes atmosphere and mood. | Highlights specific actions or scenes. |
What are the Different Types of Video Sound Effects?
There are 20 types of video sound effects categorized based on the origin of the sound, use cases, sounds from humans and animals, custom, and digitally created sounds. The diagram shows different types of video sound effects.

- Non-verbal Sound Effect
- Crowd Sound Effects
- Spot Sound Effect
- Off-Screen SFX
- Foley Sound Effects
- Isolated Sound
- Location SFX
- Environmental/Atmospheric Sound Effect
- Background Sound
- Movie Sound Effect
- Scary Sound Effect
- War Sound Effect
- Vehicle-Based sound
- Accident Sound Effect
- User Interface Sound Effect
- Cartoon Sound Effect
- Trailer Sound Effect
- Glitch Sound Effect
- Custom Design SFX
- Swoosh/Whoosh/Swish Sound Effects
1. Non-verbal Sound Effect
Non-verbal sound effects are those that come from natural activities or motions from both humans and animals. Human sounds include sneezing, coughing, footsteps, breathing, laughter, screams, and shouts. Yawns. Animal sounds include chirping, roaring, and barking to add wildlife to the scene.
2. Crowd Sound Effects
Crowd sound effects originate from the gathering of a group of people without any discernible dialogue, clapping, applauding, mourning, etc. It is often shown in scenes in the stadium, market, social gathering, etc. Crowd sound effects are often used as a background and are created by a loop group or walla during post-production.
3. Spot Sound Effect
Spot sound effect is the sound that comes from inanimate objects, window or door closing, gunshots, car brakes, etc, to synchronize the visuals. In a particular spot, the surrounding objects’ sound and noise add realism to the plot.
4. Off-Screen SFX
Off-Screen SFX is the sound outside of the camera frame that connects the context of the narrative story. It can be a hindrance to an event, indicating danger, etc.
5. Foley Sound Effects
Foley sound effects are studio-created and professionally choreographed sounds made of different materials to match the on-screen scenarios, such as clothing, door banging, footsteps, waterfalls, etc.
6. Isolated Sound
Isolated sound is one single sound vibration that deepens one particular scene, such as phone ringing, seclusion, footsteps, etc. Such sound enhances realism and makes the scenario more understandable to the viewers.
7. Location SFX
Location SFX is the sound used for introducing a specific scenario, such as busy city hustling, jungle sounds, people in a stadium, or a wedding ceremony. Location sound effects capture a particular ambience.
8. Environmental/Atmospheric Sound Effect
Environmental/atmospheric sound effect refers to sounds from every earthly element, such as wind, fire, water, snow, urban noises, birds, weather, cloud and thunder, storm, rain, landslide, etc. Environmental sound effects add realism with immersion, show changes, and establish the sense of time, environment, and mood.
9. Background Sound
Background sound, also soft sound and ambient sound, is the sound that fills up silence and makes sense to the visual context. It integrates the atmospheric foundation and empowers the foreground scenario.
10. Movie Sound Effect
Movie sound effects are the digitally created sounds used in movies, dramas, animations, and other media-produced visual narrative content to strengthen emotions, actions, scenic changes, moods, etc.
11. Scary Sound Effect
A scary sound effect is one that intensifies terror, eerie, spooky feelings, such as creepy whispers, crying sounds, haunted and muffled sounds, sudden heart-wrenching sounds, and any other unexpected noises. Scary sound clips are used in horror, thriller, and suspense movies.
12. War Sound Effect
War sound effect consists of all the sounds of a warzone, including people screaming, gunfire, marching, explosions, tanks, etc. Historical movies, war movies, games, and conflicting scenes mostly contain war sounds.
13. Vehicle-Based Sound
Vehicle-based sounds include engines, whistles, railway crossings, tracks clacking, driving, skids, car honks, boats, aircraft, etc. It makes actions, travel, and destinations more realistic.
14. Accident Sound Effect
Accident sound effects include explosion, siren, alarm, fire sounds, flame crackling, emergency signals, police, and ambulance sirens. It is used in war, action, and scientific scenes.
15. User Interface Sound Effect
The user interface sound effect is used for functional display, which includes clicks, notifications, beeps, etc.
16. Cartoon Sound Effect
Cartoon sound effect is a combination of different sound varieties such as pops, whistles, slapsticks, boings, etc, that aligns the timings of cartoon and animation.
17. Trailer Sound Effect
Trailer sound effect is a dramatic scene including rumbles, whooshes, impacts to intensify suspense, and anticipations to the movie and drama trailers, promotional contents, music videos, teasers, etc, to punctuate narrative beats.
18. Glitch Sound Effect
Glitch sound effect is digital distortion, malfunctioning, or machinery trouble, stuttering sounds that create irritation and signify underneath sounds. It is used in scenes having sci-fi or high-tech environments, data corruption, electronic failures, etc.
19. Custom Design SFX
Custom-designed sound effects are heavily processed sounds uniquely created for a single brand, stylized visuals, creative transitions, and often watermarked. It is either created by using different musical instruments, music notes, or through software.
20. Swoosh/Whoosh/Swish Sound Effects
Swoosh SFX is a dynamic, short, and air-based sound effect that is used for swiftly moving objects. It is used for transition, to create a sense of speed, and to add variation in the videos.
Why are Video Sound Effects Important in Video Editing?
Video sound effects are important for uplifting visual narratives, delivering accurate messages, emphasizing important parts, creating engaging and immersive viewing experiences, removing information barriers, and connecting viewers. The diagram shows the importance of video sound effects.

- Uplifts Visual Narratives
SFX uplifts visual narratives by reinforcing story pacing and arcs. Use of SFX makes the story more dynamic, understandable, and memorable. Refined sounds match the visual cues and emotionally resonant scenes to add weight to the plot.
- Delivering an Accurate Message
Well-placed sound delivers an accurate message, heightens the immersive feeling, and simplifies complicated concepts. It works as both a diegetic cue (sound from the story world) and a non-diegetic cue (an effect), assisting viewers to parse the actions, dialogue, scenery, intention, location, etc. Auditory icons strengthen brand identity and establish recognition.
- Emphasizing Important Parts to Navigate Viewers
Professionally crafted SFX highlights, draws viewers’ attention to key scenes, plot twists, and emotional beats. It makes changes dramatic and guides viewers’ focus, and clarifies their confusion.
- Creating Engaging and Immersive Viewing Experiences
SFX creates immersive and engaging experiences, enabling spatial audiences. It builds a 3d soundscape filled with high-quality atmospheric layers. Sounds make the visual narrative real, immersive, and interactive, making the scenes more believable.
- Removing Information Barriers
Sound effects remove information barriers by supplementing the visuals for auditory learners. It expands the audience’s accessibility to grasp content that might be missed visually. SFX holds or captures viewers’ focus during subtitle or off-screen narratives, such as accentuators and stingers, making transitions clear and practical.
- Connecting Viewers Through Evoked Emotions
Professionally designed SFX connects viewers through evoked emotions as it triggers viewers’ psychology. The psychoacoustic design technique is an example; this process in SFX manipulates sound characteristics (frequency, spatial cues, amplitude, temporal aspects, etc) which appeals to viewers’ emotions. Strategic use of tone, ambience, and environmental sounds makes human brains and ears interpret the sound in non-linear ways and craft a believable and immersive audio experience.
How Do Video Sound Effects Enhance Viewer Engagement?
Video sound effects enhance viewers’ engagement by improving their concentration on videos. Sound intensifies viewers’ auditory senses. In a 2017 research paper by the National Library of Medicine titled Understanding Why People Enjoy Loud Sound, it was stated that people’s enjoyment of sound arises via 7 general mechanisms and their interactions: a. brainstem reflexes, b. evaluative conditioning, c. emotional contagion, d. visual imagery, e. episodic memory, f. musical expectancy, and g. cognitive appraisal. Sound changes viewers’ internal physiology and psychology, conditioning them to enjoy and engage with videos. Altogether, sound affects and makes people remember what they have seen.
Are Video Sound Effects Necessary for Social Media Content?
Yes, video sound effects are necessary for social media content. It effectively delivers information in videos longer than 30 seconds. It affects how viewers understand social media videos and interact. Sounds capture their attention and stimulate thoughts, which is effective in promoting or marketing products or services.
Why are Both Sound Effects and Color Correction Important for Video Editing?
Both sound effects and color corrections are important for video editing to develop a comprehensive narrative. Using the right colors creates a perfect ambience, drives viewers’ motions, and connects them with the content message. Merging sound effects makes the narrative sensible. Accurate use of color and sound contributes to professional, on-brand, and consistent content production. It nurtures viewers’ expectations by delivering clear, engaging, understandable content.
What is the Importance of Sound Effects in Video Editing?
Sound effects in video editing are important to create a soothing aural experience for viewers. SFX aligns with visuals, making the video comprehensible and heightening viewers’ emotions and senses. Technically advanced and layered SFX elevate video quality and display professionalism by showing transitions, comic timing, and off-screen actions to follow the story’s pace. It reinforces brand identity by publishing on websites, e-commerce platforms, and social media. Cohesive sound motifs and sound palettes create unified content, ensuring auditory and visual balance and clarifying ambiguity. Expert video editors edit audio inconsistency, audio mixing issues, and unclear dialogues, and control loudness to maintain listening comfort. In films, dramas, and animated videos, sound fills the gap when visuals can’t, for example, a cappella, distorted laughter, infrasound frequency are present in horror movies, which gives off an eerie feeling, mysteries.
What is the Importance of Color Correction in Video Editing?
Color correction in video editing is important to place visual hierarchy, distinguish visual cues and elements, and increase narrative clarity for viewers. Accurate color representation enhances Footage’s appearance and ensures consistency and uniformity throughout the videos. Professional color temperatures and color palettes are maintained, ensuring polished and refined presentation, adhering to brand guidelines and commercial purposes. Professionally applied color correction in video displays controlled and seamless narrative, balancing color variations, lighting, exposure, hue, saturation, shadows, etc. The right use of color captures viewers’ mood and emotions in films, such as cool palette shows calmness, warm palettes show warmth, and black and white colors are often used for reminiscing about an event. In an animated world, exaggerated color palettes differentiate good from evil, heroes from villains, calmness from troubles.
How to Add Sound Effects to a Video?
To add sound effects to a video, follow these step-by-step guidelines:
- Open the video editing software
- Upload the video and chosen sound effects
- Place the sound
- Adjust sound characteristics
- Preview to analyze
Step 1: Open the Video Editing Software
Launch your preferred video editing software. The screenshot shows how to add keyframes to a clip for creating dramatic transitions.
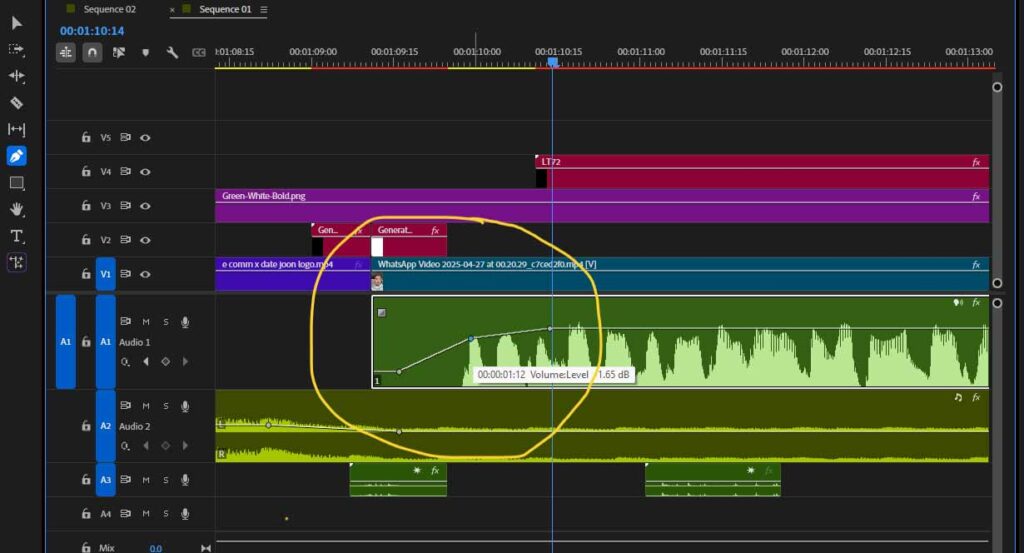
Step 2: Upload the Video and Chosen Sound Effects
Import your video file you will work on and the sound effect files you will add to the video in the software’s media library.
Make sure the sound file formats are compatible, such as MP3, WAV, AIFF, etc.
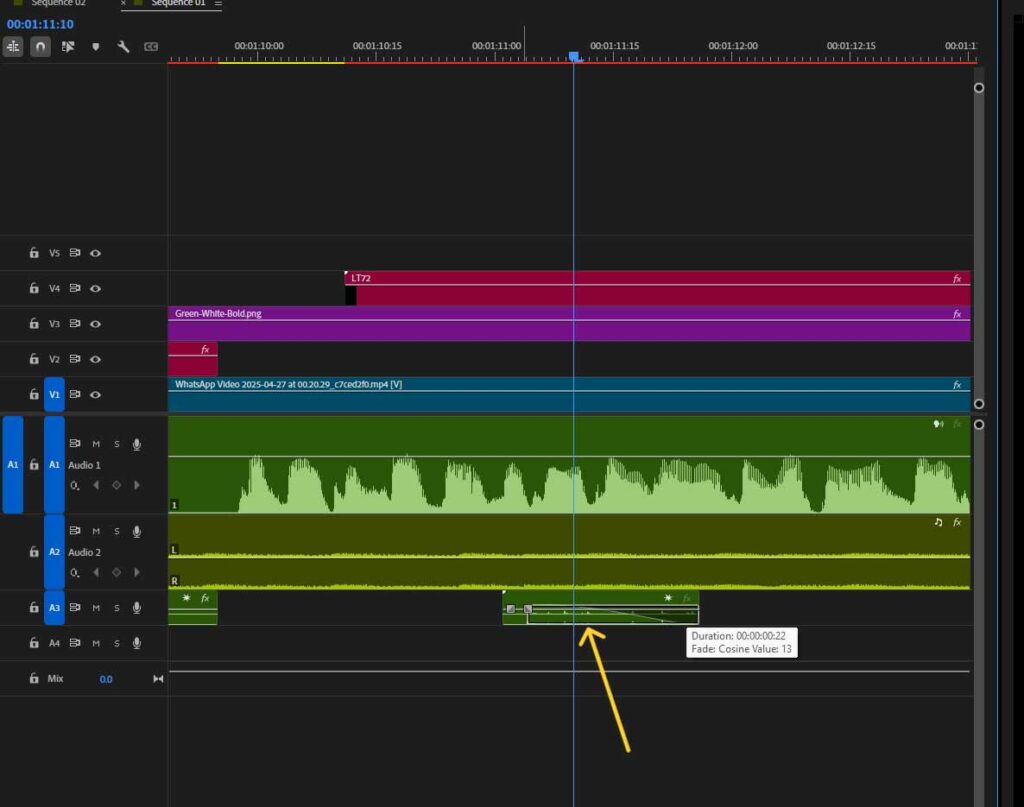
Step 3: Place the Sound
Drag the sound effect to the appropriate point of the audio timeline where you want it to synchronize with specific video actions.
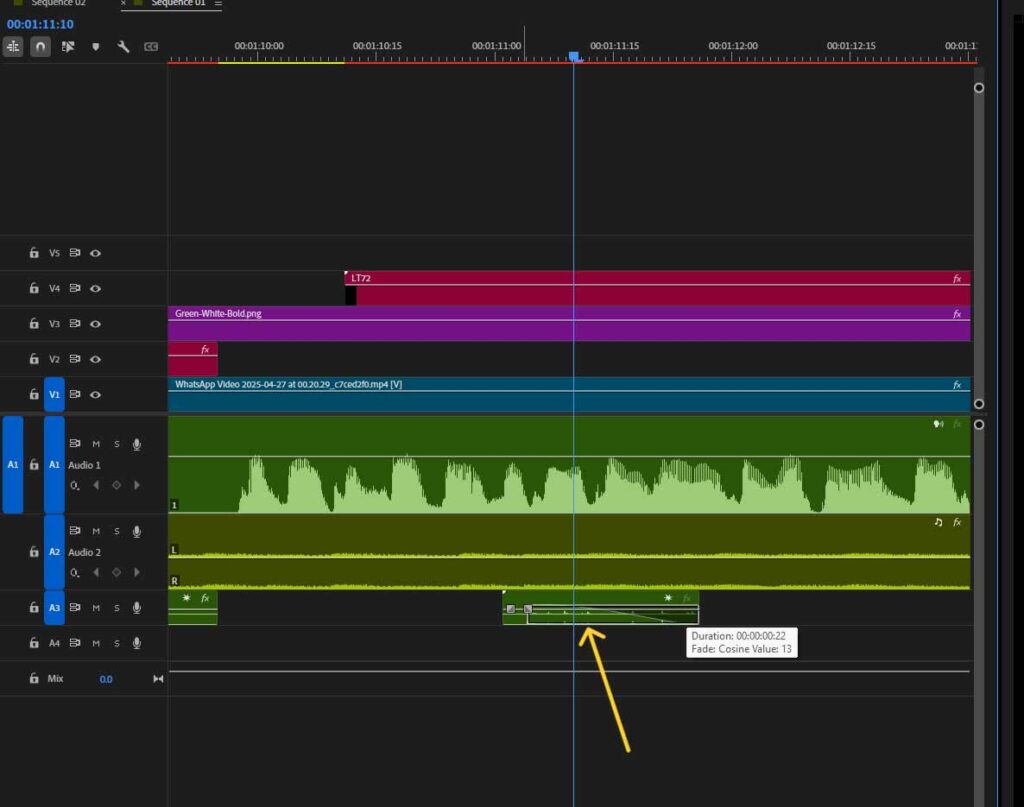
Cut or trim the audio clip to match the desired duration.
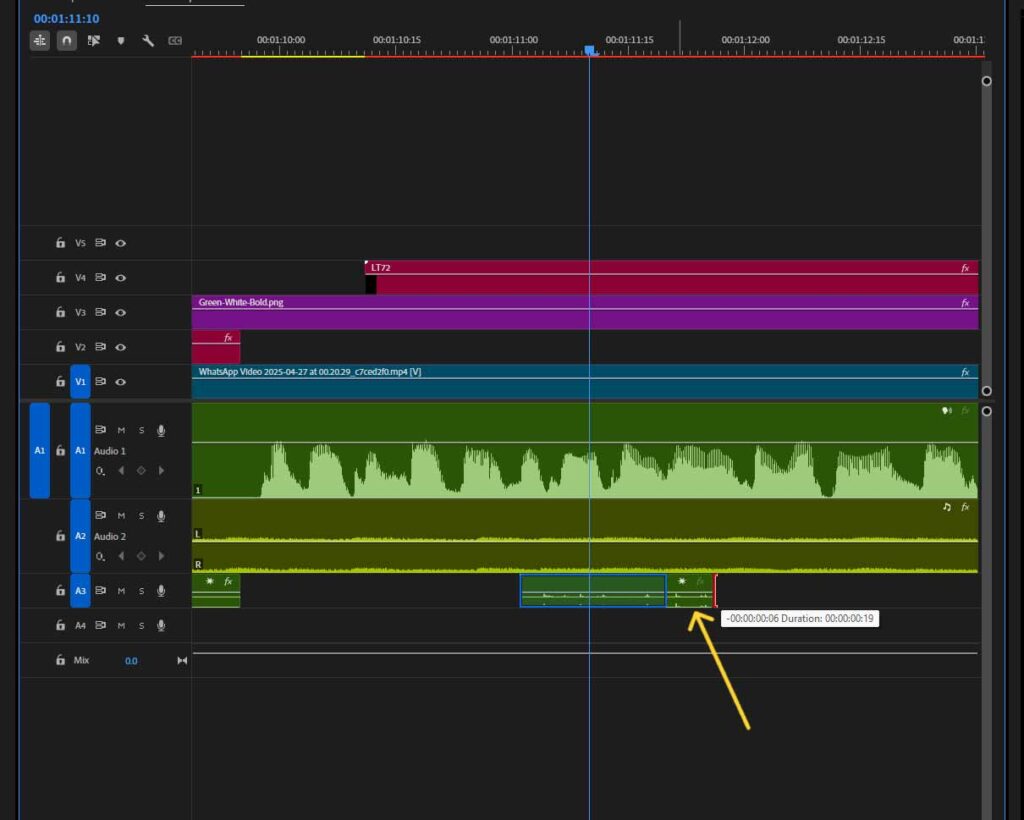
Step 4: Adjust Sound Characteristics (Volume, Speed, and Transitions)
Fine-tune the audio levels to blend naturally with existing audio.
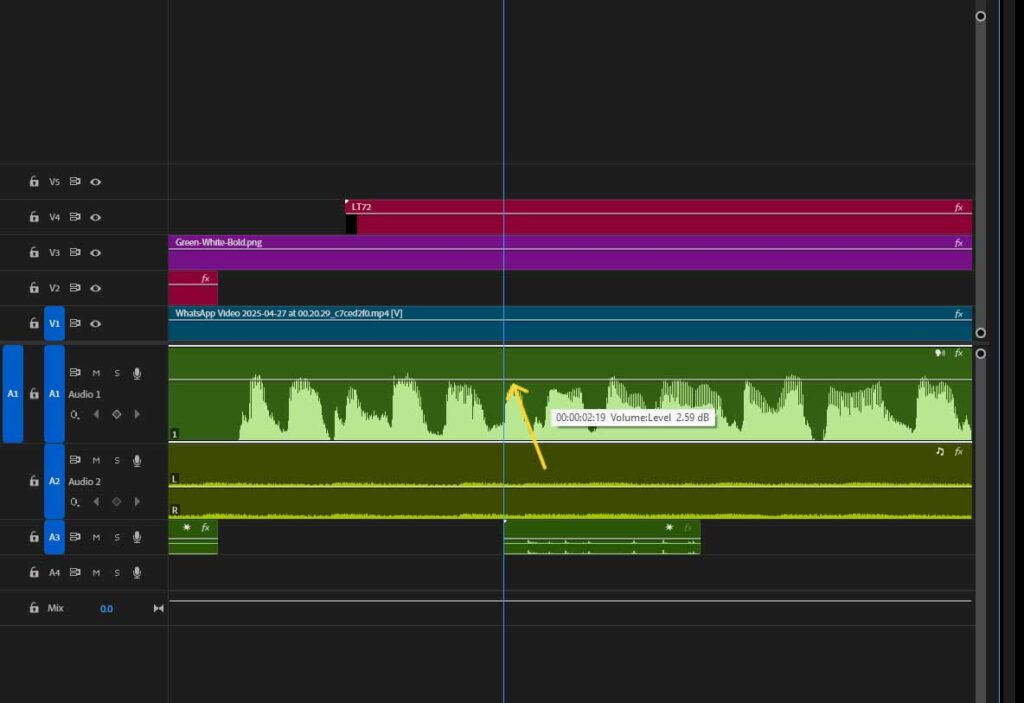
Modify the playback speed and add fade-in/fade-out effects to create smooth transitions.
Match each change aligned with the visuals.
Step 5: Preview to Analyze
Play back the entire video to check audio synchronization and overall sound quality. Once satisfied with the result, render and export the final video with the sound effects permanently integrated into the file.
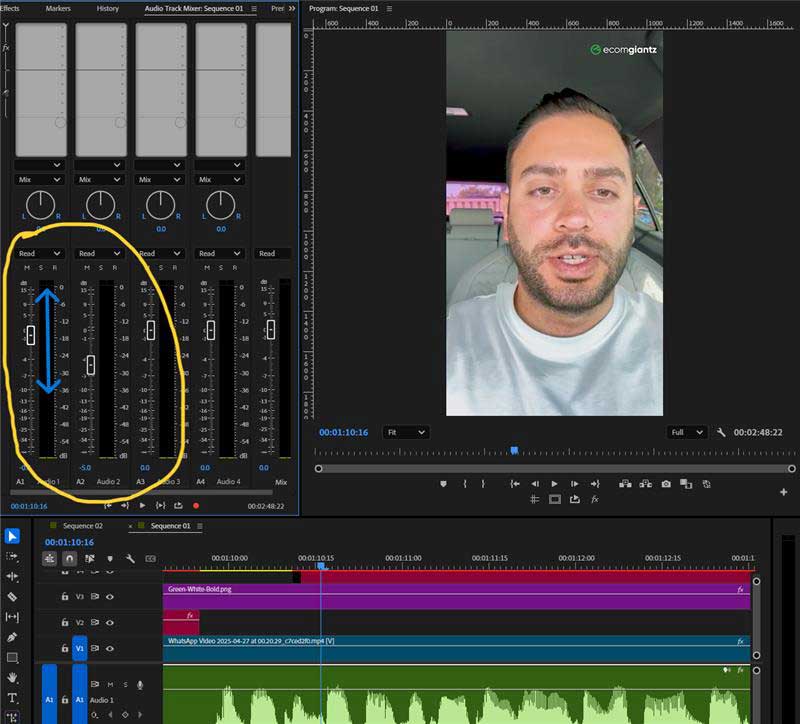
How to Adjust the Volume Level on a Video?
To adjust the volume level on a video, follow these steps.
- Find the volume level in the software’s timeline
- Select the part requiring adjustments
- Click on the volume control/audio mixer icon
- Preview for clarity
Step 1: Find the Volume Level in the Software’s Timeline
Locate the audio track or waveform display in your video editing software’s timeline panel.
Step 2: Select the Part Requiring Adjustments
Click on the specific audio segment where you want to modify the volume levels. Either select the entire audio track or just portions that need adjustment.
Step 3: Click on the Volume Control/Audio Mixer Icon
Use the volume slider, audio mixer panel, or right-click menu to increase or decrease the audio levels. Or, use keyframes or audio envelopes to create gradual volume changes or dramatic shifts at specific points in the timeline.
Step 4: Preview for Clarity
Play back the video to test the new audio levels and ensure they sound aligns with the other audio, dialogue, background music, and the whole video elements.
What is the Best Volume for Video Editing?
The best volume for video editing is to start around -12 to -14 decibels for dialogue, and -18 to -20 for music. Use calibrated monitors for sound balancing.
Do You Need High Hz for Video Editing?
Yes, you need high Hz (96kHz) when you are working on high-end music or sound design production. Using standard Hz, 48kHz is recommended as it ensures quality sounds and aligns well with video frame rate.
What File Formats are Commonly Used for Video Sound Effects?
File formats commonly used for video sound effects include MP3, AAC, OGG Vorbis, M4A (AAC), FLAC, ALAC, M4A (ALAC), WAV, AIFF, DSD, and PCM. These formats broadly fall into two categories, compressed and uncompressed files.
1. Compressed Formats: Compressed formats are audio formats that are reduced in size and are suitable for easy distribution and storage. The compressed file formats come in 2 types: lossy formats and lossless formats.
- Lossy Formats: Lossy formats are the smallest audio formats that permanently remove irrelevant data, such as MP3, AAC, etc.
- Lossless Formats: Lossless formats are the audio formats that preserve and retain sound data and quality, such as FLAC, ALAC, etc.
2. Uncompressed Formats: Uncompressed formats are the original files that store the highest sound quality and are best for post-processing. Due to containing much data, these formats require a larger space. Examples of uncompressed audio formats are WAV, AIFF, etc.
| Category | File Format | |
| Compressed | Lossy | MP3, AAC, OGG Vorbis, M4A (AAC) |
| Lossless | FLAC, ALAC, M4A (ALAC) | |
| Uncompressed | WAV, AIFF, DSD, PCM | |
1. MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer III)
MP3 is compressed audio in a lossy format that removes some audio data to reduce the size. As a result, this format is a small file which is versatile, compatible with all devices (Phone, PC) and platforms (social media, website, etc), and works fine for storing general audio, sound, and music data.
2. AAC (Advanced Audio Coding)
AAC, also known as MPEG-1 Audio Layer III and MPEG-4 AAC, is an advanced level lossy compression audio file format. It is used for better sound quality and or lower bitrates. AAC contains more detail, even in compressing and streaming platforms such as Apple Music, and YouTube supports this format.
What is the Difference Between Low Bitrate and High Bitrate?
The difference between low bit rate and high bit rate lies in sound quality. High bit rate transmits more data per second, with improved dynamics and detail, resulting in higher bandwidth requirements and clearer audio. Contrary to that lower bit rate transmits less data per second, reduced file size. Therefore, storing, transferring, and streaming are faster and efficient.
3. OGG Vorbis
OGG Vorbis is an open-source lossy audio file format. It uses the Vorbis codec inside the OGG container, which results in high-quality sound, better than MP3 at the same bitrate. OGG Vorbis efficiently compresses files, has good audio fidelity, and suits open-source apps and platforms.
4. FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec)
FLAC (.flac) is a lossless audio codec designed to compress files with fidelity. It is an open-source format and is used for streaming, archiving, and high-quality post-production. FLAC supports different channels (up to 8), bit depths from 4 to 32 bits, and sample rates of 65,535 Hz or higher.
5. ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec)
ALAC is an Apple-developed lossless audio codec format that compresses and preserves original data. This format offers a smaller file size at a lossless quality in Apple devices and is mostly compatible with Apple ecosystem-based archiving and post-production.
6. M4A (MPEG-4 Part 14)
M4A is the container; it contains sounds encoded by AAC and ALAC codecs.
- M4A (AAC): M4A (AAC) is an audio file container encoded with AAC (Advanced Audio Coding). AAC is a codec, whereas M4A (AAC) is a file container. M4A (AAC) offers high-quality audio that supports metadata with compression, such as iTunes.
- M4A (ALAC): M4A (ALAC) is an audio container format that contains ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec), providing lossless, bit-perfect compression. It is widely supported by the Apple ecosystem and offers high-fidelity audio even smaller than uncompressed WAV formats.
7. WAV (Waveform Audio File)
WAV (.wav) is an uncompressed audio data file format typically used in audio and video post-production. It stores high-resolution PCM audio data, supporting sample rates up to 192 kHz and 32-bit depth. The lossless nature of WAV has made it a useful format in film and TV sound effects, Foley, multi-layered audio editing, etc.
8. AIFF (Audio Interchange File Format)
AIFF (.aiff) is an Apple-developed uncompressed audio format that runs on both Apple-based and cross-platform systems. AIFF stores detailed metadata and is used in Mac-centric video workflows and archives.
9. DSD (Direct Stream Digital)
DSD is a high-quality audio producing format that encodes digital audio for Super Audio CD (SACD. Sony and Philips jointly developed this format. Even though it is uncompressed, it offers high fidelity. DSD is used in audiophiles, high-resolution music, etc.
10. PCM (Pulse-Code Modulation)
PCM (.pcm) is an audio encoding process that converts analog sound to a digital format. It creates raw, uncompressed audio and is best for high-fidelity sound. PCM offers versatility, is noise-resilient, and is used in DVDs and CDs.
Where to Download Royalty-free Video Sound Effects?
Download royalty-free video sound effects from Pixabay, Freesound, Premium Beat, and Envato Elements, both in free and premium versions. The graphic shows the best websites for free sound effects for video editing.

1. Pixabay
Pixabay is a library of complete royalty-free sound effects. With simple downloading options, it allows creators to access a wide range of sounds without attribution and hassle.
2. Freesound
Freesound is a community-driven database for global users. It stores unique effects, niche, and experimental clips with licensing and free.
3. Premium Beat
Premium Beat offers high-quality, curated SFXs and music tracks for videos, films, dramas, etc. It’s a paid platform backed by strong legal protection.
4. Envato Elements
Envato Elements is a part of a large creative assets subscription that offers complementary audio and SFXs, accessible through a simple licensing under a single subscription.
How to Choose the Right Video Sound Effects
To choose the right video sound effects, consider the content genre, its length, atmosphere, and the target audiences. Using the right SFX is about fine-tuning, so make variations in wavelengths and volume as well.
Wavelengths, Frequency, Volume, and Tempo
Wavelength stands for the physical length of the same point between waves. It determines how sound is perceived in video SFX.
Frequency refers to the number of waves passing, creating the pitch of the sound. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz). Low frequency has long-wavelength sounds, and high frequency has short-wavelength sounds.
| Frequency Level | Hertz (Hz) | Sound Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Low frequency | 20–250Hz | Bassy and deep, such as thunder, men’s voice, large engines, etc. |
| Mid frequency | 250Hz–4,000Hz | Warm and clear, such asmusical instruments and human voices in general. |
| High frequency | 4,000–20,000Hz | Sharp and crisp, such as whistles, bird chirps, high notes of guitars, etc. |
Note: People’s hearing range is typically 20Hz–20,000Hz and decreases with age.
Volume determines how loud the sound is. It maintains the auricular consistency of sound and dialogue flow. Sound volume is measured in decibels (dB), such as a door closing SFX is 70dB, and an explosion is 110-120dB. Professional video editors emphasize key moments by adjusting the level of the sound.
Tempo refers to the speed or pace of music videos. It is measured in beats per minute (BPM). Adjusting tempo conveys different emotions; a lower BPM means slow tempo, exuding calmness and somber feeling. On the contrary, a higher BPM evokes excitement and urgency, associated with an increased adrenaline rush.
Content Atmosphere
The content atmosphere establishes the SFX setting, environment, mood, tones, etc. Apart from using frequency variations, you can choose different color noise as an ambient background. Different types of color noise used in video SFX are as follows.
| Color Noise | Description | Characteristic | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| White (human hearing) | 20Hz–20,000Hz | Hissy noise | Tension building, masking other sounds, etc. |
| Pink | About -3dB per octave | Natural and balanced than White | Audio testing, reference mixing, etc. |
| Brown | -6dB per octave | Deep and rumbling | BGM for underwater, machinery, or sci-fi scenes |
| Blue | +3dB per octave | Sharp | Digital sound processing |
Content Genre
Choosing the right music depends largely on the video content genre. The scenario, purpose of the scene, end goal of the delivery, and message all matter while choosing the right sound. It emphasizes actions, dialogue, movements, feelings, and scenarios. The types of music, sound, or audio based on different genres are as follows.
| Content Type | Sound/Music/Audio Category |
|---|---|
| Dramas and movies | Warm, balanced frequencies, pink noise, and subtle, realistic Foley sounds. |
| Action and thriller | High-tempo and fast-paced sound. |
| Comedy and animation | Exaggerated SFX, upbeat and playful sounds. |
| Horror & suspense | Eerie sounds, infrasounds, low-frequency sounds. |
| Flying scenes | Swoosh or Whoosh sounds. |
| Commercial, promotional, and marketing videos | Clear, energetic, balanced mix of different frequencies, white and pink noise beds. |
| Corporate videos | Unobtrusive soundtracks, bright, mid-frequency, pink noise. |
| Live-action videos | Natural and environmental sound, balanced frequencies. |
Content Length
Content length should be a priority while choosing SFX for videos. SFX should sound complete. Short videos, such as ads, social media videos, contain concise, recognizable sound cues with a fast tempo. Short content SFX comes in white or pink noise to fill the silence. Long-form videos, such as YouTube videos, movies, dramas, and documentaries, have layered soundscapes, and the sound tempo varies depending on the narratives.
Target Audience
Choosing SFX differs based on target audiences, their age, location, preferences, etc.
- Children: SFX for children should be clear, high-frequency, soft, and of moderate volume. They should feel at ease and cheerful, not threatened.
- Adults: SFX for adults ranges from low to high-frequency, sophisticated layering depending on the content.
- Elderly People: SFX for elderly people emphasizes clarity, mid to low frequency, and moderate volume due to their hearing loss. Also, sounds should minimize reverberation and echo for a refined hearing experience.
- People with Visual Impairments: SFX for visually impaired people is rich with sound design, spatial audio.
What are the Best Video Sound Effects Examples?
The best video sound effects examples are as follows.
- Tom & Jerry
- Windows XP – Startup Sound
- Nike — Kyrie 3 Improv
- Nike x Spotify – Motivational Audio Ads
- Adidas Originals “SUPERSTAR” Campaign
1. Tom & Jerry
The legendary cartoon series ‘Tom and Jerry’ mostly relied on different types of sound effects, music, and minimal use of dialogue. The iconic use of SFX navigated most of the story, from the clang of frying pan to sneaky walk, banging door, whoosh sounds of running away, etc. The synergy of different audio (SFX and music) enriched the story and created an immersive experience in childhood for generations.
2. Windows XP – Startup Sound
The globally recognized sound of Microsoft’s Windows XP startup chime evoked the feeling of optimism and digital connection. Its repetition millions of times a day worldwide made it iconic. It highlighted he company’s brand message of personal technology that’s empowering, calming, and accessible.
3. Nike — Kyrie 3 Improv
The company R/GA created a genius sound concept based on improvisation. Putting Kyrie’s skills on the frame created a compelling analogy between his movements and music.
4. Nike x Spotify – Motivational Audio Ads
Nike and Spotify’s collaboration in 2023 generated a series of short and motivational audio ads that inspired girls in the UK to move. The sounds are crisp, upbeat, and dynamic, all supporting the message of possibility and hopefulness.
5. Adidas Originals “SUPERSTAR” Campaign
Adidas Originals ‘SUPERSTAR’ campaign celebrated the brand’s history. The soundtrack ‘Tears’ by Giorgio Moroder (remixed by Daft Punk and DJ Shadow) made it iconic, nostalgic, yet modern. Classic visuals with celebrity cameos were perfectly synchronized with rhythmic SFX, making it triggered people’s emotions with the brand’s heritage.

